Opinions on the 2025-26 Budget
Release Date: 2025-01-20
| Office of the Financial Secretary, | Email Delivery |
| Government of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region | budget@fstb@gov.hk |
| The People's Republic of China |
Dear Mr. Paul Chan Mo-po, Financial Secretary, and
Mr. Wong Wai-lun, Michael, Deputy Financial Secretary
Opinions on the 2025-26 Budget
Introduction:
As Hong Kong prepares to navigate the complexities of the 2025-26 fiscal year, a critical examination of its budgetary strategies is imperative. The city, renowned as a global nexus of financial and business activities, presents a fiscal structure that, while ostensibly robust, harbors inherent vulnerabilities. These vulnerabilities are underscored by the recent fiscal the Hong Kong government's official reserves stand at HKD 633.1 billion, supplemented by an additional HKD 200 billion from various funds and HKD 425.6 billion in foreign exchange reserves. This aggregates to a significant HKD 1.05 trillion in available reserves. However, beneath these impressive figures lies a series of fiscal management challenges and structural issues that necessitate a thorough exploration.
This opinion letter delves into Hong Kong's fiscal framework, scrutinizing its potential weaknesses and the risks it faces in the shifting global economic landscape. Key areas of concern include the heavy reliance on limited revenue streams, the ongoing structural deficits, and the pressing need for revenue diversification to ensure long-term fiscal sustainability. By identifying these vulnerabilities, the Hong Kong government can better position itself to weather economic turbulence and enhance fiscal resilience, securing a stable economic future in a rapidly evolving global environment.
Vulnerabilities in Hong Kong's Fiscal Structure
Hong Kong is widely recognized as a prominent global financial and business hub, with its fiscal structure appearing robust at first glance, thus providing a foundation for economic stability. However, a more in-depth analysis of its internal framework reveals that this seemingly strong economic foundation conceals significant underlying issues. Recent data indicates that the official fiscal reserves of the Hong Kong government total HKD 633.1 billion, supplemented by an additional HKD 200 billion from various funds and HKD 425.6 billion in foreign exchange reserves, culminating in approximately HKD 1.05 trillion in available free reserves. Despite these impressive figures, the financial management practices associated with them and the challenges faced merit careful examination.
This paper will investigate the fiscal structure of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region government, assessing its potential vulnerabilities and the risks it may confront in the future. Key areas of concern include the heavy reliance on specific revenue sources, the implications of ongoing structural deficits, and the critical need for diversified revenue streams to ensure long-term fiscal sustainability. By identifying these vulnerabilities, the government can better equip itself to navigate economic fluctuations and enhance its fiscal resilience in an ever-changing global environment.
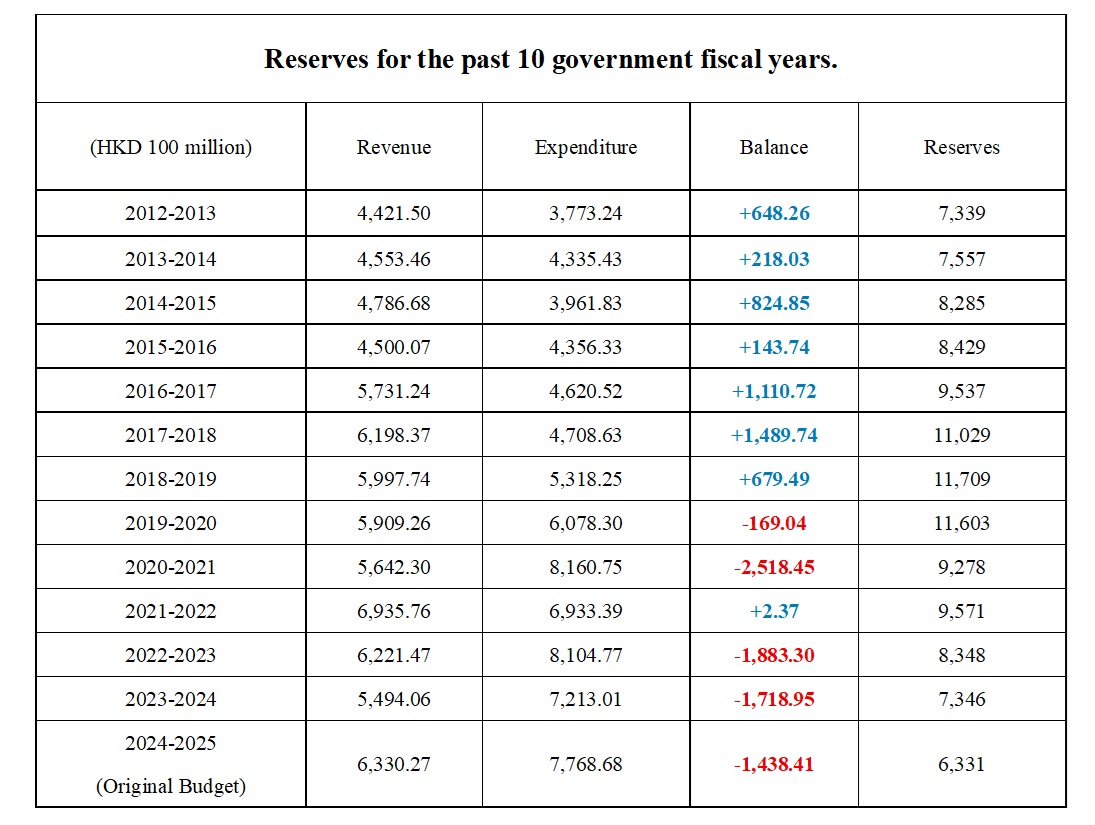
Current Status of Fiscal Reserves
Hong Kong's fiscal reserves have undergone significant fluctuations in recent years, declining from approximately HKD 1,170.9 billion in the 2018-19 fiscal year to the current level of HKD 633.1 billion. This substantial decrease raises concerns regarding the government's fiscal sustainability. While the reserves can currently be utilized to address short-term financial challenges, the ongoing fiscal deficits pose a serious concern for the long term. Government announcements made in December 2024 indicate that the projected deficit is expected to widen from the initial estimate of HKD 48.1 billion to HKD 100 billion.
In this context, the government's fiscal management appears to lack a long-term perspective, complicating its ability to effectively tackle future challenges. It is essential for the government to adopt more strategic and sustainable financial policies that not only address immediate fiscal needs but also ensure the stability and resilience of Hong Kong's economy in the years ahead. Emphasizing long-term planning and innovative approaches will be crucial in reinforcing fiscal health amid evolving economic circumstances.
Risk of Revenue Source Monopolization
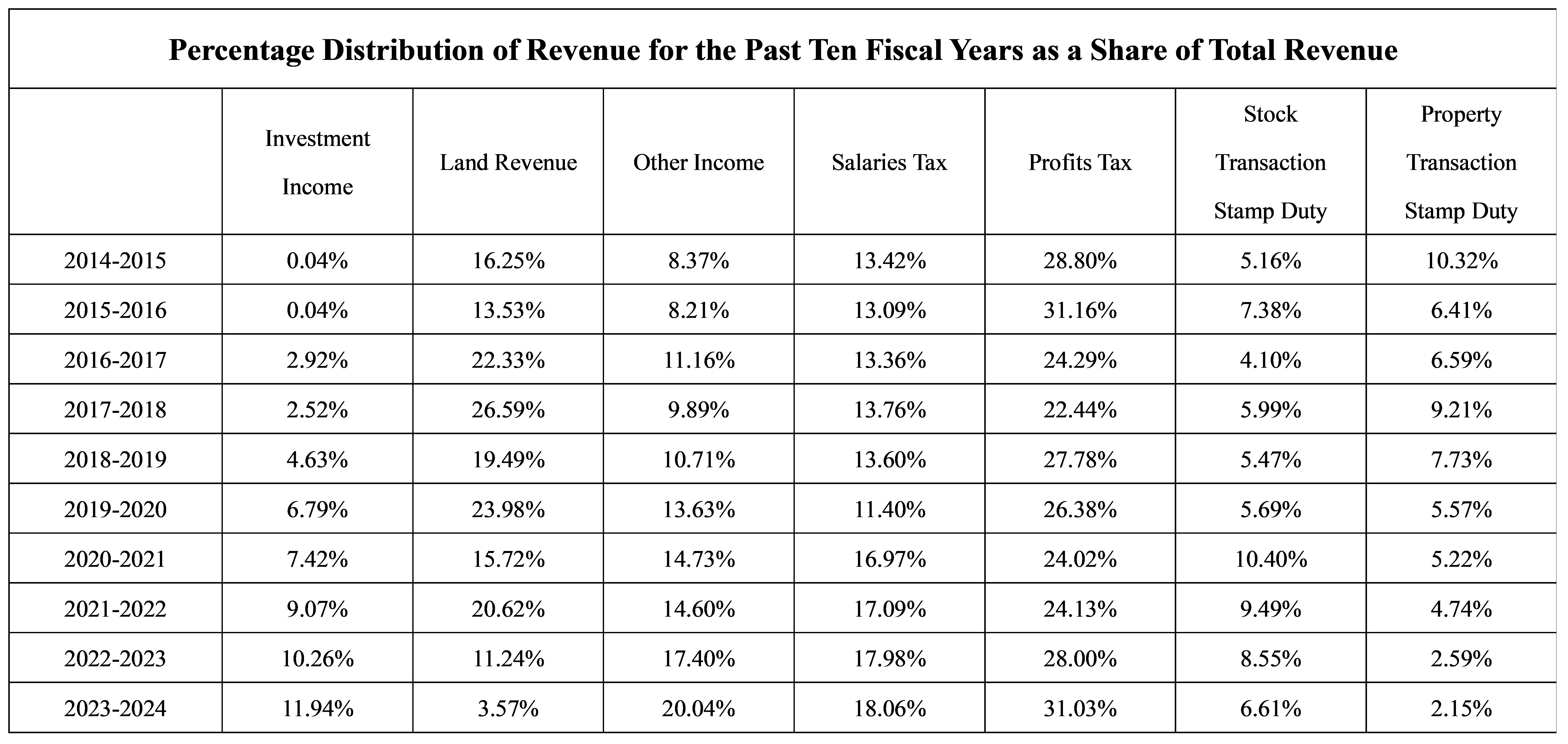
While the revenue sources for the Hong Kong government may seem diversified, they are predominantly dependent on a few key components: profits tax, salaries tax, land revenue, and stock transaction stamp duty. This relatively narrow revenue structure exposes the government to vulnerabilities in the face of economic fluctuations and market changes. A particularly concerning trend is the significant decline in land revenue: in the fiscal year 2017/18, land revenue averaged HKD 164.8 billion, constituting 26.6% of total government revenue. However, this figure plummeted to HKD 80 billion in subsequent years and further decreased to HKD 19.6 billion in the fiscal year 2023/24, representing only 3.6% of total government revenue—the lowest level recorded since the 2008 financial crisis.
This drastic decline not only affects the government’s fiscal surplus but also underscores the potential for a financial crisis in the future. To ensure fiscal stability and resilience, it is crucial for the government to diversify its revenue sources and develop strategies that mitigate the risks associated with reliance on a limited number of income streams. By broadening its revenue base, the government can enhance its capacity to withstand economic shocks and maintain financial health over the long term.
Worsening Structural Deficit
The Hong Kong government has experienced fiscal deficits for five consecutive years, with the deficit for the fiscal year 2023/24 reaching HKD 143.8 billion—1.5 times higher than the preliminary budget estimate. This situation highlights the government's inadequacies in addressing the structural fiscal deficit. Continuous deficits require the implementation of more prudent strategies concerning both expenditure and revenue; however, actual policy execution has been slow and lacking in innovation. Such management practices undoubtedly undermine the foundation of fiscal reserves, further exacerbating the financial risks that may arise in the future.
To effectively address this structural deficit, it is crucial for the government to adopt a more proactive and strategic approach, emphasizing long-term sustainability and fiscal resilience. This may involve reevaluating expenditure priorities, enhancing revenue generation methods, and cultivating a more dynamic economic environment capable of adapting to changing conditions. Without decisive action, the ongoing structural deficit could lead to significant challenges for Hong Kong's fiscal health and economic stability in the years to come. Establishing a robust framework for fiscal management will be essential to navigating these complexities and ensuring a sustainable financial future.
Expanding the Tax Base for Diverse Fiscal Revenue Development
Hong Kong's tax system is recognized for its simplicity and low tax rates, with no obligations to pay taxes or military expenses to the central government. According to data from the Census and Statistics Department, there are 17 types of taxes, including four direct taxes and three indirect taxes that are no longer levied. However, tax revenues are heavily concentrated on land revenue, property transaction stamp duty, and stock transactions. The volatility of these three revenue sources is closely linked to economic cycles, rendering them unstable and potentially leading to high costs that impede industry development and diminish international competitiveness.
To address the current narrow fiscal revenue sources, the government should actively explore ways to expand the tax base beyond capital gains tax, aiming for a healthier and more balanced fiscal income. This could involve introducing new tax categories or revising existing ones to encompass a broader range of economic activities, thereby ensuring more stable revenue streams.
Furthermore, regarding expenditure, consideration should be given to whether civil servants should share the burden during challenging economic periods. This may involve reviewing public sector salaries, benefits, and overall spending to ensure that fiscal resources are utilized efficiently and equitably. By adopting a comprehensive approach to both revenue generation and expenditure management, the government can enhance its fiscal resilience and foster sustainable economic growth, positioning Hong Kong for long-term stability and prosperity.

Stock Transaction Stamp Duty
Hong Kong finds itself in the unenviable position of having the highest stock transaction stamp duty in the world. The government's consistent reluctance to engage in tax competition with rival markets raises pertinent questions, particularly in light of recent developments such as the abolition of the minimum commission system within the securities sector and the establishment of the Competition Commission. Our Association strongly advocates for a reevaluation of the stock transaction stamp duty, stressing that any proposed changes must not hinder the trading of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs).
We propose that a potential reduction in the stock transaction stamp duty be considered in tandem with the reintroduction of stamp duties on derivative instruments, including warrants and bull-bear certificates. This dual approach could create a more equitable environment for stock investors while simultaneously stimulating market activity. In essence, while tax reduction proposals have the potential to invigorate the market, any increases in taxation risk curtailing growth. Enhancing Hong Kong's standing in the international arena is likely to attract greater public backing for government initiatives.
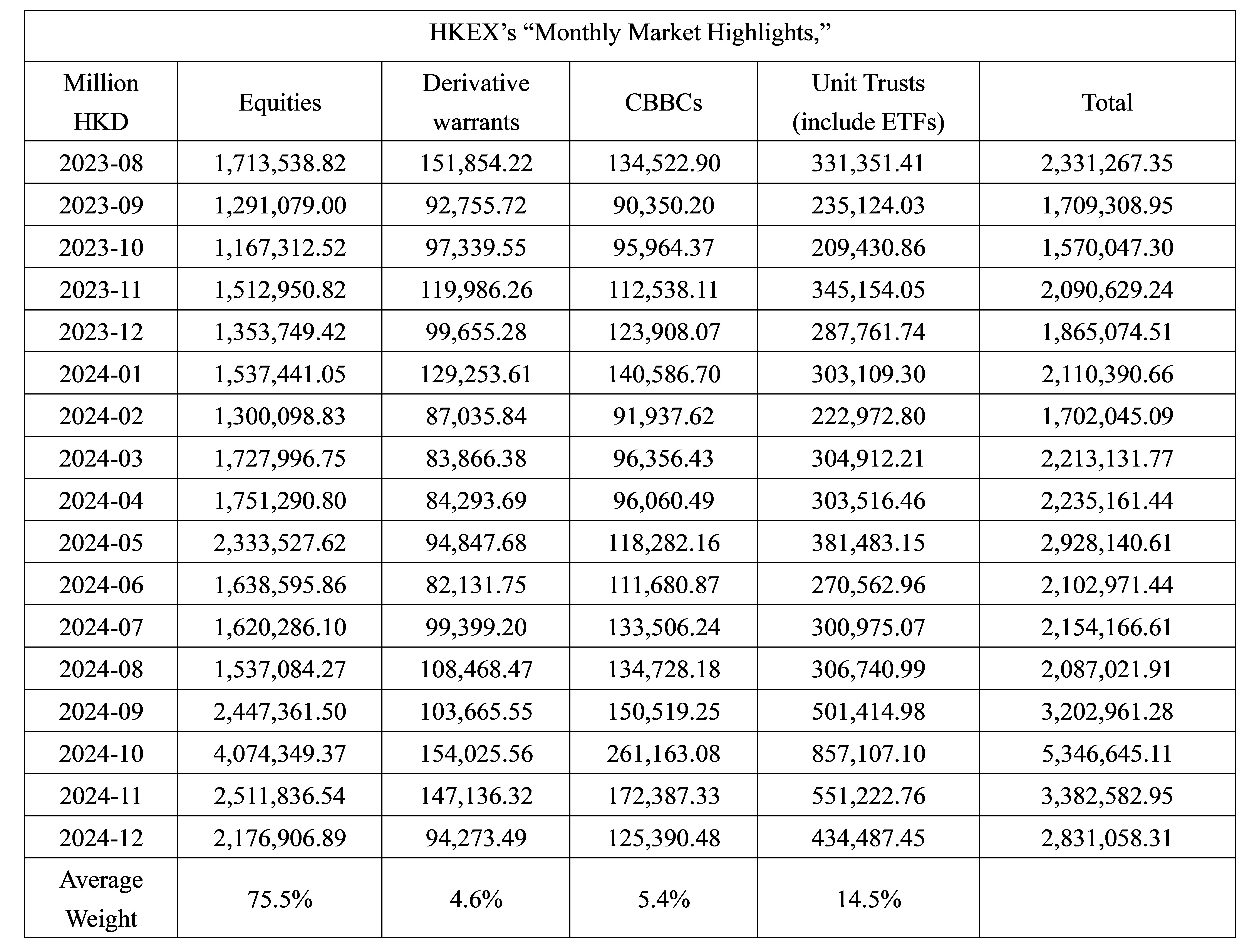
Our Association has meticulously analyzed data from the HKEX’s “Monthly Market Highlights,” focusing on the period from August 2023 to December 2024, which spans a total of seventeen months. The findings reveal that stocks constituted an average of 75.5% of total market turnover, while derivative warrants accounted for 4.6%, bull-bear certificates represented 5.4%, and unit trusts made up 14.5%.
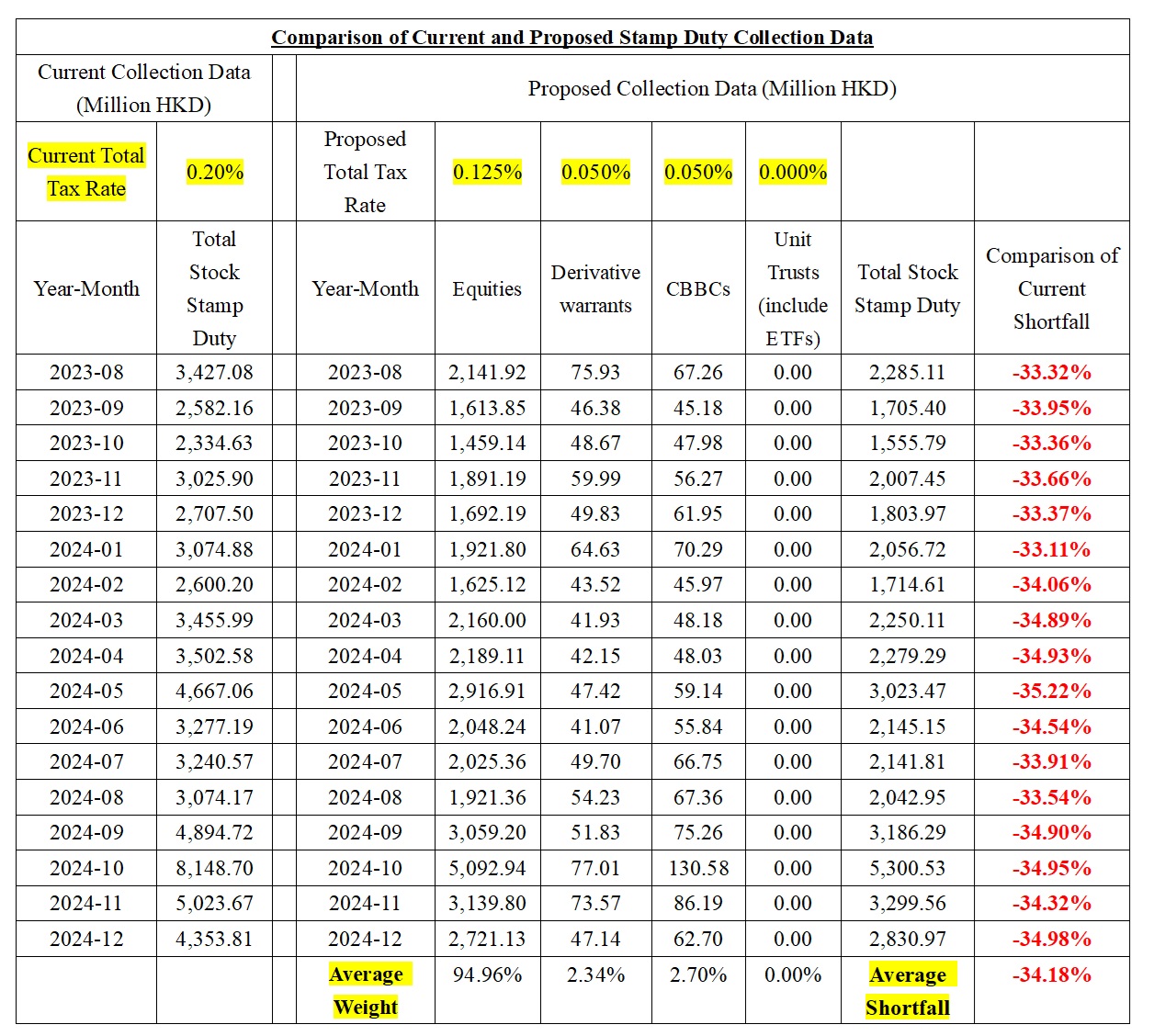
To optimize the current tax structure, we recommend revising the existing arrangement where both buyers and sellers are subject to a 0.1% duty, proposing instead a reduced rate of 0.0625% for both parties. For derivative warrants and bull-bear certificates, we suggest implementing a rate of 0.025% for both buyers and sellers. Based on our calculations derived from the past 17 months of data, this adjustment could yield an average reduction of 34% in total stock stamp duty collection. Detailed data supporting these recommendations is available for further examination and review.
Our Association recognizes the complex fiscal landscape currently confronting the government. It is essential, however, to skillfully navigate the delicate balance between the pressing economic realities and the unpredictable nature of the securities market. With urgency and purpose, we implore the government to seriously consider our recommendations, particularly the expansion of the tax base. This crucial move could effectively alleviate the risks associated with a narrow revenue stream, paving the way for a more diverse financial foundation. Such an adjustment would not only ease the burden of infrastructure costs but also fortify Hong Kong's commitment to sustainable development.
Furthermore, our association emphasizes a critical objective: the complete abolition of the stock stamp duty. This transformative action has the potential to significantly enhance the competitiveness of our international securities market, positioning it as a powerful contender on the global stage. Within this dynamic interplay of fiscal strategy and market responsiveness lies a promising pathway toward a more resilient economic future, one that can withstand the challenges of an ever-evolving landscape.
The shadow of economic prospects
In the coming years, the challenges confronting the Hong Kong government will extend well beyond mere fiscal deficits, encompassing a spectrum of issues such as decelerating economic growth, an aging populace, and the unpredictable nature of the global economic environment. Should Hong Kong's economy and real estate sector continue to stagnate, we may face a protracted fiscal deficit that could ultimately precipitate a crisis of resource depletion. Although current fiscal reserves may appear sufficient, their sustainability is likely to be rigorously tested as deficits escalate, raising significant concerns regarding future economic viability.
While the fiscal framework of the Hong Kong government may outwardly project a strong economic foundation, it conceals critical vulnerabilities tied to structural deficits and various economic challenges. A lack of proactive management in terms of revenue generation and expenditure has stymied effective diversification of income sources, thereby posing substantial risks to fiscal sustainability. In this uncertain economic landscape, the financial resilience of the Hong Kong government will face formidable challenges. It is only through transparent and responsible fiscal governance that Hong Kong can hope to preserve its esteemed status as a global financial hub and protect the welfare of its citizens moving forward.
As the budget proposal draws near, we earnestly hope that the government will thoughtfully consider the perspectives of diverse stakeholders, including this council. In a spirit of patriotism and unwavering dedication to Hong Kong, we aim to collaborate on fostering economic development and crafting practical solutions for the future.
Recommendation for the Government to Guarantee Bond Issuance to Facilitate Financing for SMEs
In the context of ongoing global economic instability, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Hong Kong are grappling with significant financing challenges. These enterprises serve as vital pillars of the local economy, contributing greatly to innovation and employment. Despite their importance, many SMEs are encountering substantial obstacles in securing the financial support they require, particularly as banks tighten their lending standards during economic downturns—a situation aptly described by the adage “closing umbrellas when it rains.”
To alleviate these financing difficulties, we strongly recommend that the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government take proactive measures to facilitate the issuance of bonds. This initiative should be supported by local chambers of commerce and Hong Kong chambers located across various regions of Mainland China, thereby providing SMEs with more reliable and stable financing channels.
Data from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority reveals a tentative improvement in the financing landscape during the first quarter of 2024; however, the approval rates for bank loans remain challenging. Many enterprises continue to struggle with the loan application process. Concurrently, the Hong Kong best lending rate has decreased from 5.88% at the end of July 2023 to 5.38% in November 2024, which creates a favorable market environment for bond issuance.
By guaranteeing bond issuance for SMEs, the government can enhance access to capital, fostering a more resilient economic landscape that empowers these vital enterprises to thrive even in uncertain times. This strategic move would not only bolster the financial stability of SMEs but also promote broader economic growth throughout Hong Kong.
Proposed Plan
1. Recommendation for Chambers of Commerce to Participate in Bond Issuance Guaranteed by the HKSAR Government:
- Collaboration and Guarantee: We propose that the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government guarantees the issuance of specialized bonds and actively collaborates with chambers of commerce to encourage their members and SMEs in Hong Kong to participate. This initiative aims to specifically assist capable SMEs that have faced significant challenges in recent years, thereby enhancing their capacity to secure financing while simultaneously reducing their overall cost of capital.
- Use of Funds: The proceeds from these bonds should be strategically allocated to support the business expansion of SMEs across several critical areas, including international trade, global supply chain services, technological innovation, green transformation, and digital upgrades. By channeling funds into these sectors, we can not only bolster the growth potential of SMEs but also contribute to the broader economic development of Hong Kong in a sustainable manner.
This proposed plan stands to fortify the financial resilience of SMEs, ensuring they remain integral contributors to Hong Kong's economic landscape while navigating the complexities of a challenging global environment.
2. Attracting Participation from Private Equity Funds and Consortiums:
- Involvement of Private Equity Funds: We recommend that private equity funds establish dedicated consortiums to engage in this initiative. These consortiums can offer flexible funding solutions along with professional management expertise, enabling SMEs to utilize the raised funds more effectively. By leveraging the resources and networks of private equity funds, SMEs can access not only financial support but also strategic guidance that can enhance their operational efficiency and growth potential.
- Investment Opportunities: The plan aims to attract private equity funds and consortiums by presenting competitive investment returns. While the associated risks may be elevated, the implementation of appropriate asset allocation and risk management mechanisms can effectively safeguard the interests of investors. By clearly outlining the potential for returns alongside robust risk mitigation strategies, we can create an appealing proposition for private equity involvement, ultimately fostering a collaborative environment that benefits both investors and SMEs.
3. Funding Application and Distribution Mechanism:
- Chamber Channels: Member enterprises of the chambers of commerce should be allowed to submit funding applications through their respective chambers. This process would involve preliminary reviews and recommendations by the chambers, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of fund distribution. By leveraging the existing networks and knowledge of the chambers, the government can ensure that funding is directed toward the most viable and deserving SMEs.
- Government-Managed Application Channel: To ensure inclusivity, a government-managed application channel should be established for SMEs that are not members of any chamber of commerce. This channel will provide all eligible enterprises with equal access to funding opportunities, ensuring that no deserving SME is left out of the financing framework.
- Supporting the Future Development Engine of Hong Kong through Healthy Growth of SMEs: To encourage responsible borrowing and timely repayments, funds can be prioritized and offered at preferential interest rates to SMEs that have demonstrated a consistent record of timely repayments over the past five years. This approach not only supports their cash flow but also incentivizes good financial practices, contributing to the overall stability and growth of the SME sector.
4. Policy Support and Transparent Regulation:
- Policy Assurance: The government should provide essential legal and policy support to facilitate the compliant issuance of bonds. This should include offering tax incentives and administrative conveniences that promote ease of access for SMEs to participate in the bond issuance process. Such measures will not only incentivize SMEs to engage with the funding initiative but will also ensure that the funds are utilized effectively and in alignment with regulatory requirements.
- Transparent Regulation: It is crucial to establish a public and transparent oversight mechanism that regularly reports to the public on the initiative's progress and the utilization of funds. This transparency will enhance trust among all stakeholders, including investors, SMEs, and the general public, fostering a collaborative environment that encourages participation and accountability.
By guaranteeing the issuance of bonds and attracting private equity funds to form consortiums, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government can create a stable and flexible financing environment for SMEs. This approach will empower these enterprises to navigate economic challenges and pursue sustainable development effectively. Moreover, this initiative will not only bolster the competitiveness of SMEs but also contribute to the overall recovery and growth of Hong Kong's economy.
We urge the government to thoroughly assess the feasibility of this proposal and collaborate closely with chambers of commerce and financial institutions to ensure the effective implementation of the plan. Together, we can foster a resilient economic landscape that supports the vital role of SMEs in driving Hong Kong's future prosperity.
Strategic Analysis and Detailed Proposal for the Hong Kong Government to Fully Acquire Octopus Holdings Limited
In the backdrop of rapid global digital economic development, electronic payment has become an indispensable part of modern urban life. As an international financial center, Hong Kong boasts a superior financial infrastructure and an innovative environment. “Octopus” is a pioneer in Hong Kong's electronic payment market, underscoring its importance. This article proposes that the Hong Kong government fully acquire Octopus Holdings Limited and explores its detailed economic benefits, implementation steps, and strategic significance.
Market Position and Valuation of Octopus Holdings Limited
Since its establishment in 1997, Octopus has maintained a leading position in Hong Kong's electronic payment market. By the end of 2022, Octopus achieved an annual revenue of HKD 1.6718 billion and a net profit of HKD 613.3 million. Its extensive market applications cover public transport, retail, dining, and other service industries, with over 20.7 million cards in circulation. Based on its stable profitability and market advantage, Octopus's valuation can be assessed using the price-to-earnings (P/E) method.
Assuming a P/E ratio of 15, the valuation is calculated as follows:
Valuation=HKD 613.3 million×15=HKD 9.1995 billion
This valuation provides a financial benchmark for the government acquisition.
Acquisition Cost Analysis
The ownership structure of Octopus is complex, with MTR Corporation holding 86.12% of the shares, and the Hong Kong government holding 75.28% of MTR Corporation, which means the government indirectly holds 64.84% of Octopus. To achieve full acquisition, the government needs to purchase the remaining 35.16% of shares. Based on the valuation of HKD 9.1995 billion, the cost for the government is:
Acquisition Cost=HKD 9.1995 billion×0.3516=HKD 3.233 billion
Deposit Management and Financial Strategy
The deposits charged to commercial users by Octopus are one of its important funding sources. Assuming a deposit of HKD 2,000 per Octopus machine and a total of 46,000 merchants, the total deposits would amount to HKD 920 million. As of 2017, with over 34.5 million Octopus cards in circulation, each card having a deposit of HKD 50, the total deposits collected would amount to HKD 1.725 billion. The total deposit calculation is as follows:
If these deposits are placed in a bank with an annual interest rate of 3.5%, the annual interest income would be:
Interest Income = HKD 2.645 billion × 3.5% = HKD 92.57 million.
This income can be used to subsidize Octopus's operational costs and further support the development of electronic payment infrastructure.
Promoting Digital Hong Kong Dollar and E-currency Adoption
Following the full acquisition of Octopus, the government could seamlessly integrate its payment platform with the “Digital Hong Kong Dollar,” significantly enhancing the adoption of digital currency. In 2024, Octopus began waiving the transaction fee for the first HKD 10,000 of monthly transactions for merchants using the business version of the app. This policy benefits over 80% of merchants by significantly reducing transaction costs for small and medium enterprises.
Additionally, more than 25,000 taxi drivers have installed the commercial version of the Octopus app, providing a solid foundation for digital currency application in the transportation sector. Promoting digital currency will reduce cash circulation, lowering cash management costs for merchants and improving operational efficiency.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Despite the significant potential benefits of acquiring Octopus, the government must address the following risks:
1. Market Competition Pressure: With the rise of other payment platforms, Octopus needs to continually innovate to maintain competitiveness.
2. Technology Upgrade Needs: Electronic payment technology is rapidly evolving, requiring government investment to ensure the Octopus system's advancement and security.
3. Public Reaction: Government intervention in private enterprises may draw public attention, necessitating effective communication and transparent management.
Long-term Benefits and Strategic Significance
Fully acquiring Octopus will not only consolidate Hong Kong's leading position in the electronic payment market but also drive the digital transformation of society as a whole. By lowering transaction costs and enhancing payment efficiency, Hong Kong's SMEs will become more competitive in the global market. This move aligns with the government's long-term strategy to promote digital economic development, laying a solid foundation for Hong Kong's sustainable economic growth.
Conclusion
The Hong Kong government's full acquisition of Octopus Holdings Limited is a strategic decision with far-reaching impacts. By integrating resources and guiding policy, the government can promote the widespread adoption of digital currency while supporting SME development and enhancing Hong Kong's international competitiveness. This initiative will not only bring significant economic benefits to Hong Kong but also foster the digital transformation of society, fueling future economic growth.
Strategies for Improving Hong Kong's Financial Market: Drawing Inspiration from the U.S. Experience
Introduction
As an international financial center, Hong Kong must continuously strive to maintain its competitiveness and adapt to the evolving dynamics of the global market. To achieve this goal, it is essential to analyze the differences between Hong Kong and the United States in key areas such as exchange diversity, financial market access, margin requirements, listing thresholds, regulatory oversight of fiscal resources, and anti-money laundering standards. By leveraging the successful experiences of the U.S., Hong Kong can optimize its financial market structure and regulatory framework, ultimately enhancing its global standing.
Promoting a Diverse Exchange Markets
Currently, Hong Kong relies on a single securities exchange, which to some extent limits market competition and vibrancy. The United States boasts up to 13 exchanges, including the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ, and this diversified structure encourages market competition and innovation. If Hong Kong can introduce more exchanges, it would not only reduce trading costs but also attract more international capital inflows, further consolidating its position as a global financial center.
Implementing a multi-exchange system would provide investors with more choices and enhance liquidity, creating a more dynamic trading environment. Additionally, it could foster niche markets for specific sectors, thus promoting broader economic growth and diversification.
Enhancing Flexibility in Market Access
The entry requirements of the U.S. financial markets, particularly regarding technological capabilities and financial health, provide companies with an efficient and transparent environment. In contrast, while Hong Kong's requirements for local knowledge and ongoing professional training ensure a high standard of professionalism, they may also hinder the entry of international enterprises.
To address this, Hong Kong should consider increasing the flexibility of its market access while maintaining professional standards. This could involve streamlining the application processes, offering alternative pathways for compliance, and recognizing international qualifications. By doing so, Hong Kong can attract a wider range of international participants, fostering a more diverse and competitive market landscape. This approach would not only enhance the city's appeal as a financial hub but also stimulate innovation and collaboration across borders.
Enhancing Margin and Risk Management Practices
When it comes to margin and risk management, the United States stands out with its intricate regulations that offer precise guidance to the market. In contrast, Hong Kong's streamlined requirements cater primarily to newcomers, providing an accessible entry point. However, there lies an opportunity for growth. By adopting more advanced risk management frameworks and drawing inspiration from the methodical approach to margin ratios utilized in the U.S., Hong Kong could significantly bolster market transparency and stability. This strategic evolution would not only refine existing practices but also empower investors with a deeper understanding of risk, ultimately fostering a more robust financial ecosystem.
Revising Listing Thresholds to Foster Innovation
The U.S. market's low threshold policy for startups creates an inviting landscape for innovative enterprises, offering them the freedom to flourish. In stark contrast, Hong Kong's current listing requirements—especially those centered on profitability—pose significant barriers that could stifle the growth of pioneering firms. To ignite a wave of innovation, Hong Kong ought to contemplate a recalibration of its listing thresholds, particularly for select industries. Such a move would not only draw in a greater number of inventive companies but also enrich the market’s competitiveness and diversity, ultimately positioning Hong Kong as a vibrant hub for groundbreaking ideas and ventures.
Fortifying Financial Resource Regulation
The FINRA framework in the United States exemplifies a remarkable flexibility in adjusting capital requirements tailored to diverse circumstances, presenting a valuable reference for Hong Kong. As it seeks to uphold market stability, Hong Kong stands at a crossroads where it can delve into more dynamic capital regulation strategies—strategies that are responsive to the unique needs of various financial institutions. By embracing this adaptability, Hong Kong could not only reinforce its regulatory framework but also cultivate a more resilient and versatile market landscape, effectively positioning itself in the global financial arena.
Streamlining Compliance Mechanisms for Greater Efficiency
In the bustling landscape of Hong Kong, where anti-money laundering regulations loom large and stringent, the intricate web of compliance requirements can often weigh heavily on businesses. The United States, conversely, adopts a procedural compliance model that presents a more navigable framework, easing the burdens on enterprises. To bolster its international allure, Hong Kong ought to consider a strategic simplification of select processes, all while steadfastly upholding its rigorous compliance standards. This endeavor could significantly alleviate the compliance costs that businesses currently grapple with, paving the way for a more vibrant and accessible market environment.
Conclusion
To maintain its esteemed stature in the global financial arena, Hong Kong must embrace a relentless pursuit of reform and innovation. By scrutinizing the market structures and regulatory practices of the United States, Hong Kong stands to significantly elevate its financial system, invigorating market dynamism and amplifying international competitiveness. This proactive approach is essential; only by adapting to the evolving landscape can Hong Kong sustain its pivotal role amidst the swift currents of global finance. In doing so, it will cultivate a more transparent and efficient market environment, ultimately benefiting investors and businesses alike, and ensuring its relevance in an ever-changing world.
Private Equity and Venture Capital Funds
As a pivotal financial center in Asia, Hong Kong has long been a magnet for international private equity (PE) and venture capital (VC) funds, thriving within its well-established financial system and steadfast rule of law. The presence of these funds not only catalyzes local economic growth and job creation but also solidifies Hong Kong's role as a vital conduit, linking global capital to the burgeoning Asian markets. Yet, as the market environment evolves and global economic fluctuations persist, Hong Kong's PE and VC funds now confront a myriad of challenges.
A recent report by PwC highlights a notable deceleration in the growth of Hong Kong's private equity market from 2022 to 2023, particularly within the venture capital segment. Total investments in this sector plummeted from approximately $8 billion in 2021 to under $5 billion in 2023, marking a staggering decline of 33%. Moreover, early-stage financing for startups has become increasingly arduous, especially when compared to more favorable environments like Singapore. These statistics underscore the significant ramifications of global economic uncertainty and structural shifts within the market, revealing the pressing need for strategic adaptation within Hong Kong's investment landscape.
Global Economic Uncertainty and Its Impact on Market Confidence
The aftermath of the pandemic has cast a long shadow over the global economic landscape, profoundly influencing Hong Kong's investment market. Factors such as the sluggish pace of interest rate reductions and escalating geopolitical tensions have collectively dampened the sentiment among global investors, exerting considerable pressure on fundraising efforts and the return potential of various funds.
Despite the U.S. Federal Reserve's decision to decelerate rate hikes in the latter half of 2023, the prevailing high interest rate environment continues to disrupt global capital flows. This situation poses particular challenges for private equity funds that operate in U.S. dollars, as soaring financing costs emerge as a significant obstacle within the industry. According to the South China Morning Post, many private equity funds encountered substantial difficulties in fundraising during 2023, with Hong Kong's share of total fundraising in the Asia-Pacific region plummeting from approximately 15% in 2021 to below 10% in 2023.
Compounding these challenges are the geopolitical tensions that have further strained the investment climate. The ongoing deterioration of U.S.-China relations has eroded global confidence in the Hong Kong market, directly impacting investors' capital commitments. A study conducted by the China Center for International Economic Exchanges (CCG) revealed that in 2023, more than 30% of multinational funds chose to relocate their capital to Singapore as a strategy to mitigate geopolitical risks. These mounting challenges necessitate a thorough reassessment of Hong Kong's strategy for attracting foreign investment, particularly against the backdrop of an increasingly unstable global economic environment.
Weakness in the Secondary Market Hinders Primary Market Development
In Hong Kong, equity investment funds predominantly target the primary market, seeking returns by investing in unlisted companies and anticipating valuation increases. However, the sluggish performance of the secondary market has reverberated through the primary market, with particularly notable effects on the Pre-IPO fund sector.
The year 2023 marked a significant downturn in IPO activity on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, reaching levels not seen in nearly a decade. According to Deloitte, total IPO fundraising in Hong Kong for 2023 dwindled to approximately HKD 26 billion, a staggering drop from the peak of HKD 430 billion in 2021. This decline has directly impacted the investment returns of Pre-IPO funds, many of which now face the grim prospect of losses upon exit, leading to a pronounced contraction in Pre-IPO investment scales.
A case in point is the listing of technology companies from mainland China. In recent years, numerous domestic firms have pursued Pre-IPO financing in Hong Kong. Yet, due to the plummeting valuations at the time of listing in 2023—where some tech companies saw their market values dip to less than 50% of their original valuations post-IPO—instances of funds reporting losses upon exit have become increasingly common. A senior executive from a Shenzhen private equity fund remarked to the Economic Daily that enthusiasm for Pre-IPO funds has waned significantly over the past year, prompting some funds to suspend operations and redirect their focus toward other investment opportunities.
This detrimental impact extends beyond Pre-IPO funds, affecting other private equity and venture capital entities as well. As liquidity in the exit market diminishes, a growing number of funds are adopting a wait-and-see approach, further exacerbating overall market liquidity issues and perpetuating a damaging cycle that stifles investment potential across the board.
Regulatory Pressure and Escalating Compliance Costs
The stringent regulatory framework has historically been a hallmark of Hong Kong's financial market, bolstering investor confidence and market integrity. However, as compliance requirements continue to escalate, operational costs for funds are also rising significantly. In 2023, the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) heightened its scrutiny of private equity funds, particularly regarding cross-border capital flows and anti-money laundering (AML) measures. This shift has compelled fund management companies to invest more resources into their internal control departments to ensure adherence to these regulations.
According to a report by UBS, the annual compliance costs for private equity funds in Hong Kong average 2.5% of total fund assets, notably higher than the 1.2% observed in Singapore. This increased compliance burden not only diminishes Hong Kong's allure as a financial hub but also prompts some funds to contemplate relocating their operations to jurisdictions with lower compliance costs.
In addition to rising compliance expenses, regulatory constraints on merger and acquisition (M&A) transactions have further stifled market vitality. Market participants have expressed concerns that Hong Kong's regulations governing corporate M&A activities are excessively stringent, leading to protracted approval processes that heighten transaction uncertainty and associated costs. This situation often results in many deals failing to meet their deadlines. While such regulations may serve to mitigate risks in the capital markets to some extent, they concurrently suppress capital liquidity and undermine the competitiveness of Hong Kong's market, ultimately hindering its potential for growth and innovation.
Revitalizing Market Vitality
To rejuvenate Hong Kong's private equity and venture capital markets, it is essential for both the government and market participants to implement a comprehensive set of measures aimed at improving the current landscape.
Firstly, enhancing the vitality of the secondary market is paramount. Adjusting stamp duty appropriately can significantly lower overall transaction costs and stimulate market activity. The introduction of increased stamp duty in 2021 serves as a pertinent example; it resulted in a rapid decline in trading volume, underscoring the importance of reducing stamp duty to bolster trading engagement.
Secondly, a moderate relaxation of margin trading policies is a critical initiative worth considering. The tightening of margin trading regulations has considerably constrained the financing capabilities of growth enterprises on the Growth Enterprise Market and smaller mainboard companies, thereby reducing interest in Hong Kong listings among SMEs. Easing these policies could attract more short-term investors into the market and provide companies with additional financing avenues, fostering a gradual recovery of the overall market.
Furthermore, the government's funding policies should embrace greater diversification. For funds targeting emerging industries such as fintech, healthcare, artificial intelligence, and green energy, the introduction of direct financial subsidies or tax incentives could effectively attract global venture capital funds to establish a presence in Hong Kong. Continuous optimization of funding programs will be vital in drawing increased capital inflows, thereby promoting the growth of innovative enterprises.
Hong Kong's private equity and venture capital markets are currently navigating a critical transformation phase. While they face numerous challenges—including global economic uncertainty, a sluggish secondary market, and stringent regulations—these obstacles also offer opportunities for reform and innovation within the capital market.
By enhancing capital market liquidity, optimizing regulatory frameworks, and strengthening governmental support for enterprises, Hong Kong can swiftly reclaim its status as a premier investment hub in Asia. Crises often pave the way for transformation, and the future success of Hong Kong's financial landscape hinges on the collaborative efforts of the government, enterprises, and market participants. Together, they can revitalize Hong Kong's equity investment market and restore its competitiveness on the global capital stage.
Regarding Futures
In a recent annual policy address, the Chief Executive articulated a bold vision: transforming Hong Kong into a premier hub for commodity futures. This ambition resonates deeply within the industry, which eagerly anticipates a comprehensive roadmap from the government—one that delineates supportive policies and robust financial backing in the forthcoming budget.
Delving into the numbers, the average daily trading volume for futures and options during the first eleven months of 2024 reached an impressive 140,000 contracts. This figure marks a notable increase of approximately 16% compared to the same timeframe the previous year. Interestingly, index futures dominate this landscape, accounting for over 80% of all futures trading activity in Hong Kong, while other commodity futures lag behind in engagement.
Consequently, industry stakeholders are fervently hoping that the new budget will usher in a multifaceted approach to bolster the commodity futures market. They are particularly focused on the establishment of supportive policies, enticing tax incentives, and the enhancement of market infrastructure.
Herein lie pivotal recommendations and forward-looking prospects:
1. Tax Incentives for Commodity Futures
To invigorate the commodity futures landscape, the government might contemplate a strategic reduction or even a complete exemption of stamp duty and associated taxes on transactions. This move would effectively lower trading costs, enticing a broader spectrum of market participants and fostering increased engagement within the sector.
Additionally, implementing profit tax incentives could significantly enhance the attractiveness of the market. By offering tax reductions or beneficial schemes for companies involved in commodity futures trading, both local and international players would be encouraged to dive into this burgeoning market. Such initiatives would undoubtedly stimulate trading activity, paving the way for a more dynamic and robust commodity futures environment.
2. Support for Market Infrastructure
To bolster the commodity futures market, the government should contemplate the establishment of a dedicated fintech development fund. This fund would specifically cater to the needs of fintech companies focused on creating innovative trading platforms and technologies tailored for commodity futures. Such an initiative would not only enhance trading efficiency but also fortify security measures within the market.
Moreover, integrating cutting-edge technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence can usher in a new era of transaction transparency and operational efficiency. These technologies could facilitate the development of smart contracts, which would streamline trading processes and significantly reduce associated costs.
In tandem with these initiatives, government support for the development of futures exchanges is crucial. By providing targeted funding or policy assistance, existing exchanges could expand their market reach and enhance their operational capabilities. This would result in a broader array of trading options for commodity futures, ultimately heightening market competitiveness and attracting diverse participants.
3. Promotion and Education
To elevate the profile of the commodity futures market, it is imperative that the government, in collaboration with futures exchanges, spearheads a series of educational and promotional initiatives. By organizing seminars, workshops, and informative sessions, they can effectively disseminate crucial knowledge about commodity futures. Such efforts would significantly enhance public awareness and deepen the understanding among market participants regarding the intricacies and opportunities within this sector.
Furthermore, forging partnerships with higher education institutions and vocational organizations is essential. The government should champion the development of specialized professional courses focused on commodity futures. This initiative would not only equip aspiring professionals with the necessary skills but also elevate the overall professional standards within the market. By enhancing the qualifications of industry practitioners, the sector would benefit from a more knowledgeable and capable workforce, ultimately driving growth and innovation in commodity futures trading.
4. Market Diversification
As global markets continue to intertwine, Hong Kong stands poised to emerge as a preeminent futures trading hub in Asia, attracting a diverse array of international investors. To realize this potential, the Hong Kong government and exchanges must amplify their collaboration with other leading financial centers, thereby streamlining the feasibility of cross-border commodity futures trading and delivery mechanisms.
Moreover, in response to the escalating market demand for sustainable and environmentally conscious products, Hong Kong has an opportunity to innovate by developing commodity futures that align with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. By introducing products from emerging markets—such as carbon credits and sustainable agricultural commodities—Hong Kong can broaden the spectrum of available futures, tapping into a growing niche that prioritizes sustainability.
Additionally, it is vital to provide robust support for Hong Kong's exchanges and financial institutions to participate in international financial exhibitions. Such engagement would not only showcase Hong Kong's capabilities but also bolster its global image as a leading center for commodity futures trading, fostering greater recognition and investment in the region.
5. Regulatory Environment
In light of the swift evolution of fintech and its profound impact on the market, existing regulatory policies have found it challenging to keep pace with these advancements. To address this gap, it is essential for the government, exchanges, and regulatory bodies to adopt a flexible and responsive approach. This involves dynamically adjusting relevant policies in alignment with market developments and emerging demands, ensuring that the regulatory framework remains attuned to the ever-evolving landscape.
Regulatory agencies should proactively revise existing rules to reflect current market dynamics while simultaneously establishing a clear and coherent regulatory framework. This framework must aim to provide a stable and transparent environment that fosters confidence among market participants. Additionally, creating a comprehensive legal structure is crucial for safeguarding the rights and interests of all stakeholders involved. By doing so, the regulatory environment will become more conducive to growth, ultimately enhancing the attractiveness and viability of the commodity futures market.
6. Commodity Warehousing
A compelling proposal envisions the establishment of a dedicated spot commodity delivery site and warehouse on the vacant land at the Kwai Chung Container Terminal. By leveraging the inherent logistics advantages of this prime location and designating it as a bonded area, Hong Kong can significantly enhance its role in the commodity trading landscape. This initiative would not only utilize Hong Kong's robust financial services sector—bolstered by an array of professional financial, legal, and logistics service providers—but also ensure comprehensive support for commodity trading activities.
Moreover, Hong Kong's strategic geographical position at the heart of Asia serves as a catalyst for trade with Mainland China and other neighboring countries. This advantageous location, combined with an established transportation network and sophisticated logistics infrastructure, amplifies the efficiency of goods transportation and distribution across the region.
As a prominent global financial center equipped with a mature financial market, a robust legal framework, and a seamless settlement system, Hong Kong is ideally situated to facilitate financing and settlement processes for commodity trading. The development of dedicated commodity warehousing facilities would pave the way for positioning Hong Kong as a leading hub for commodity futures trading.
In conclusion, if the forthcoming budget can effectively bolster the commodity futures market through these initiatives, it stands to attract a greater influx of both domestic and international investors. This surge in activity would enhance the competitiveness of Hong Kong's commodity futures market, further entrenching its status as a vital financial center. Such strides would not only strengthen market competitiveness but also cultivate a sustainable environment for long-term market development and investment.
Regarding to the Investor Compensation Fund
In recent months, advertisements have proliferated across the vibrant landscapes of Hong Kong, Kowloon, and the New Territories. One particularly striking image features a cheerful pink pig clutching a shield adorned with the character “存,” which translates to “save.” This lively mascot heralds the recent elevation of the bank deposit protection limit to an impressive HKD 800,000. My friend has expressed admiration for the safety of Hong Kong's banks, feeling reassured while engaging in the buying and selling of securities. However, my friend is unaware that Hong Kong also has another financial protection scheme—the Investor Compensation Fund, which specifically safeguards investment matters and offers a higher limit than the bank deposit protection.
The Investor Compensation Fund (hereafter referred to as the Compensation Fund) is under the stewardship of the Securities and Futures Commission and commenced operations alongside the enactment of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571) in 2003. This single fund effectively consolidated three previous compensation schemes: the Stock Exchange Compensation Fund, the Futures Exchange Compensation Fund, and the Dealer Margin Scheme.
The primary objective of the Investor Compensation Fund is to provide a safety net for investors of all nationalities who incur losses due to the misconduct of intermediaries, such as licensed brokers. The compensation limit is set per investor: for those holding securities accounts, the compensation limit stands at HKD 500,000, while a similar cap applies to futures account holders facing broker misconduct. This means that an investor with both securities and futures accounts under the same broker could potentially claim up to HKD 1,000,000, surpassing the bank deposit protection limit.
Moreover, the Compensation Fund extends its coverage beyond just securities and futures contracts traded on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange; it also includes A-shares traded via the Stock Connect scheme. Compensation amounts are determined based on the closing price of the relevant securities or futures contracts at the time of the misconduct. It is crucial to note that misconduct refers specifically to actions such as broker insolvency, bankruptcy, fraud, or embezzlement, rather than market fluctuations or declines.
Investors who have suffered losses and wish to seek compensation can submit their claims to the Investor Compensation Company, which meticulously manages these claims. The application process is clearly outlined on their website, where the Company assesses whether misconduct has occurred and if the claimant qualifies for compensation. If a claimant contests the decision, they may appeal to the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal.
Unlike the deposit protection scheme, which sees banks ultimately bearing the costs of compensation, the Compensation Fund is financed primarily through transaction levies imposed on investors during securities or futures trading. This levy system includes a mechanism that allows for the suspension or resumption of levy collection based on the net asset value of the fund. Since 2005, the levy has been suspended, and in 2020, the maximum compensation amount was raised from HKD 150,000 to HKD 500,000 to accommodate significant growth in investor assets and maintain a compensation coverage level of approximately 80%.
The current Securities and Futures Ordinance imposes rigorous oversight on licensed brokers, leading to occasional complaints from industry insiders. Brokers must adhere to stringent financial resource regulations, comprehensive financial reporting requirements, and internal controls, such as disclosing the benefits of sale products and assessing clients’ suitability for investment. Despite challenging market conditions and fierce competition, many brokers have managed to navigate operations smoothly without resorting to the Compensation Fund. In fact, since the Fund established on 2003, with only six claims invitations issued since the fund's inception, illustrating the stability of licensed brokers and the protective role of the fund.
Yet, amid the prominence of the deposit protection scheme, the Investor Compensation Fund remains relatively obscure, leaving many investors unaware of their rights and protections. While it is unlikely that the government intentionally prioritizes one sector over another, the lack of visibility for the Compensation Fund raises questions. Why is there a concentrated effort to promote the deposit protection scheme while the broader protective measures for investors in Hong Kong are overlooked? Why aren’t the benefits of investor protection plans more effectively communicated to strengthen investor confidence and enhance the competitiveness of the market? These pertinent questions warrant careful consideration and action from relevant authorities to bolster investor trust in the landscape of Hong Kong's financial markets.
Sources: Legislative Council documents, Securities and Futures Commission, Investor Compensation Company.
Suggestions regarding listing regulations
1. Enhance the Listing System for Greater Appeal
To draw in a diverse array of high-caliber enterprises, particularly those flourishing in dynamic sectors like hard technology and biotechnology—already thriving on prominent domestic and international exchanges—it's imperative to refine our approach. Imagine the potential of instituting a streamlined dual listing mechanism, designed to entice these innovative companies to actively trade their shares on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. By implementing such strategic initiatives, we can significantly enrich the pool of quality investment opportunities available in the Hong Kong market, ultimately amplifying its allure and competitive edge within the global financial arena.
2. Refine the Investor Landscape in the Hong Kong Stock Market
To invigorate participation from a broader spectrum of qualified mainland investors in the Hong Kong stock market, it is essential to bolster the interconnectivity between these two markets. This could involve fine-tuning the Shanghai-Hong Kong and Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect mechanisms, making them more user-friendly and efficient. Additionally, lowering the barriers and costs associated with mainland investors' entry into Hong Kong stocks can create a more inviting environment. Such enhancements are poised to catalyze a significant influx of capital into the Hong Kong market, diversify the investor demographic, and ultimately stimulate vibrant market activity that resonates with both local and international stakeholders.
3. Amplify Promotion and Education for the Hong Kong Stock Market Among Investment Institutions
To cultivate a robust influx of long-term value investors—think pension funds and sovereign wealth funds—it's crucial to intensify efforts in promoting the Hong Kong stock market while simultaneously educating both domestic and international investment institutions. By fostering a deeper understanding of the market's unique strengths and potential, we can bolster investor confidence and awareness. Such initiatives will not only stabilize market sentiment and enhance valuations but also establish the Hong Kong stock market as a premier destination for discerning investors seeking sustainable growth and long-term returns. Through strategic outreach and educational programs, we can create a compelling narrative that resonates with these pivotal financial entities, ensuring their ongoing engagement and investment.
4. Enhance Overall Liquidity in the Hong Kong Stock Market
As we approach the conclusion of the U.S. interest rate hike cycle, a unique opportunity arises to invigorate liquidity within the Hong Kong market and elevate valuations. It is essential to implement forward-thinking policies, such as entirely abolishing the stock stamp duty, which would significantly diminish the costs tied to high-frequency trading. This strategic move is anticipated to unleash a wave of trading activity, fostering a more dynamic and vibrant market environment. By capitalizing on these developments, we can not only enhance liquidity but also attract a wider array of participants, ultimately strengthening the overall resilience and appeal of the Hong Kong stock market.
5. Strengthen Cooperation and Communication with International Markets
To bolster the international competitiveness and influence of the Hong Kong market, it is vital to strengthen cooperation and communication with global financial arenas. By actively engaging with key international stakeholders and fostering strategic partnerships, we can create a synergistic effect that enhances the overall appeal of the Hong Kong market. This collective effort has the potential to significantly improve the valuation landscape of the Hong Kong IPO market, paving the way for a resurgence that positions it back at the forefront of global financial hubs. Through these collaborative initiatives, we aim not only to elevate market stature but also to instill renewed confidence among investors, ensuring a robust and dynamic future for Hong Kong's financial ecosystem.
6. Propose a Temporary Reduction in Minimum Market Capitalization Requirements for Main Board Listings
In light of the current sluggish market conditions, where many industries are grappling with low price-to-earnings ratios, the existing stipulations for listing on the Hong Kong Main Board—specifically, the minimum profit requirement of HKD 35 million and the market capitalization threshold of HKD 500 million—may hinder potential applicants. This requirement, reflecting a historical price-to-earnings ratio of 14.3 times, presents a significant barrier, even for those who meet the profit criteria. To invigorate the Hong Kong IPO market, it is advisable to temporarily reassess and reduce the minimum market capitalization requirements for qualifying applicants. By doing so, we can foster a more inclusive environment that encourages new listings and enhances the overall dynamism of the market, ultimately contributing to a more vibrant and competitive financial landscape.
7. Advocate for the Relaxation of Listing Regulations Concerning Newly Injected Assets by Listed Companies
The current framework governing anti-takeover actions delineates specific scenarios—namely, changes in control of a listed company and substantial asset acquisitions aimed at new controlling shareholders or their associates within a 36-month window surrounding such changes. These stringent regulations may inadvertently stifle growth and innovation among listed companies. Therefore, it is prudent to reevaluate the stipulations surrounding anti-takeover measures, particularly by relaxing the listing regulations concerning newly injected assets. Such adjustments could significantly enhance the attractiveness of Hong Kong's listing environment, fostering a more dynamic market that revitalizes the value of listed companies. By encouraging strategic asset injections, we can bolster investor confidence and position Hong Kong as a more appealing destination for corporate growth and investment.
Government Bond Issuance as Revenue
1. Assessment of Bond Issuance Scale and Effectiveness
The scale of bond issuance must be carefully considered, and a thorough evaluation of future repayment capacity is essential before deciding to issue bonds. It is crucial to rigorously assess the effectiveness of debt utilization, ensuring that borrowed funds are directed toward projects that can provide sustainable and stable returns while also delivering significant social and economic benefits. This approach helps avoid investment in unprofitable ventures, which could lead to a debt repayment crisis in the future.
For example, funding in education and technological research and development can effectively enhance the quality of human resources in Hong Kong and improve innovation capabilities, laying a solid foundation for future economic growth. Similarly, investing in infrastructure upgrades, such as transportation, can significantly enhance urban operational efficiency and competitiveness.
Conversely, funds should not be easily allocated to projects lacking clear profit prospects, those with high risks, or initiatives of minimal strategic significance to Hong Kong. Such investments could lead to economic inefficiencies and make future debt repayment challenging, potentially resulting in a debt trap.
2. Enhancing Financial System and Information Transparency
To cultivate a more transparent financial management framework, it is essential to adopt an Accrual Basis for fiscal budget preparation and to establish a routine public reporting mechanism regarding the territory's debt situation. This comprehensive disclosure should encompass intricate details about the scale of the debt, its intended purposes, repayment strategies, and other pertinent information. By elucidating Hong Kong's financial standing in such a manner, we can significantly bolster public confidence and trust in the region's fiscal health.
Furthermore, by stabilizing market expectations through enhanced transparency, we can solidify Hong Kong's reputation within the international financial landscape. Such proactive measures not only foster a sense of accountability but also enhance the credibility of the financial system, ultimately reinforcing the territory's image as a reliable and transparent hub for global investors.
3. Diversifying Revenue Sources and Streamlining Expenditures
The urgent need for comprehensive revenue-generating and cost-saving strategies cannot be overstated. In terms of revenue generation, it is critical to look beyond traditional taxation and bond issuance. Significant efforts should be directed towards fostering the development of new industries through targeted policy support and tax incentives. For example, actively nurturing emerging sectors such as the digital economy and green finance can broaden the high-value-added service industry in Hong Kong, creating new economic growth points and additional sources of taxation.
On the expenditure side, establishing a dedicated team within the auditing department to conduct thorough reviews of government expenditures is recommended. This initiative aims to identify and eliminate unnecessary administrative costs and inefficient investments. By optimizing government operational processes, we can enhance administrative efficiency and reduce the consumption of human and material resources.
Moreover, exploring diversified financing channels is essential for mitigating debt risks. For future large-scale infrastructure projects, reliance on a single bond financing model should be minimized. Instead, actively pursuing public-private partnership models can leverage the strengths of private enterprises in funding, technology, and management expertise, thereby complementing government resources. Additionally, attracting foreign investment for Hong Kong's construction and development is crucial. By formulating favorable policies and creating a conducive investment environment, we can draw in international capital, alleviate funding pressures, and introduce advanced technologies and management practices, ultimately supporting the internationalization of Hong Kong's economy.
4. Industry Expansion and Broadening the Tax Base
As Hong Kong advances in developing its bond market, a proactive strategy is essential for ensuring the sustainable recovery of long-term revenue streams. It is crucial to actively seek effective methods for reasonably broadening the tax base, particularly in response to the significant challenges posed by structural fiscal deficits. Strengthening the unique scale and diversity of Hong Kong's industries has become an urgent priority.
Investing in and supporting sectors such as cultural and creative industries, healthcare, and high-end manufacturing is vital for fostering local brands and enterprises. This will enhance their competitiveness and standing within the global supply chain. By providing policy guidance and integrating resources, the government can facilitate collaborative development across various industries, creating cluster effects that lessen the dependence on traditional sectors like finance and real estate.
By fundamentally solidifying Hong Kong's fiscal revenue base through the establishment of a diversified and sustainable industrial structure and income system, the economy will gain resilience against the complexities of the global economic landscape. This strategic approach will ensure the long-term stability and healthy operation of Hong Kong's economy, positioning it for sustainable growth and prosperity.
Regarding Digital Finance
1. Support the Construction of Digital Financial Infrastructure
Promote the development of Cyberport and Hong Kong Science Park to attract more FinTech companies, including Virtual Asset Trading Platforms (VATP) and various Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) firms in Hong Kong. Offering tax incentives can encourage international FinTech companies to establish regional headquarters or research and development centers in the region.
Enhance the application infrastructure for technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data within the financial sector. Optimize Hong Kong's digital payment infrastructure to facilitate the interoperability of cross-border payment systems, particularly in collaboration with mainland China (e.g., the “Cross-Border Wealth Management Connect”).
Additionally, it is advisable to take inspiration from the Singaporean government, which has allocated a reserve fund of HKD 400 million to directly support the development of innovative technologies, especially cryptocurrency platforms.
· Providing Direct Support for the Development of Blockchain Technology in the Industry
To foster the growth of blockchain technology within various industries, a comprehensive support framework is essential. This framework should include the following initiatives:
- Specialized Funding: Allocate dedicated funds specifically for the development and deployment of blockchain technology. This funding should support initiatives related to smart contracts, digital asset trading, and cross-border payment solutions, which are crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and transparency in transactions.
- Funding for FinTech Startups: Increase financial backing for FinTech startups by offering low-interest loans or innovative grants. This support will assist these emerging companies in developing solutions such as digital payments, InsurTech, and RegTech, thereby contributing to the overall advancement of the financial technology ecosystem.
- Encouragement of Blockchain Applications: Actively promote and support the development of blockchain applications in areas such as corporate financing and asset management. By facilitating the integration of blockchain technology, businesses can improve their operational processes and increase trust among stakeholders.
- Funding for Cybersecurity R&D: Provide financial support for research and development initiatives focused on cybersecurity infrastructure related to digital finance. Emphasis should be placed on preventing cyberattacks and data breaches, ensuring that the adoption of blockchain technology does not compromise the security of financial transactions and sensitive data.
· Investing in Digital Currency Infrastructure:
- Amplifying Resources for e-HKD: Propel the financial backing for research initiatives and pilot projects centered around the “e-HKD” (the digital Hong Kong dollar). This strategic enhancement aims to catalyze the broader adoption of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), ushering in a new era of digital finance that intertwines innovation with practical application.
- Synergy with Digital Renminbi: Foster a robust partnership in conducting cross-border payment trials alongside Mainland China's “Digital RMB.” This collaborative endeavor seeks to fortify the financial nexus with the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, paving the way for seamless transactions and an integrated economic landscape that transcends borders.
2. Supporting the Development of Digital Assets, Especially Virtual Assets
- Refining the Regulatory Landscape: Continuously enhance the regulatory framework governing virtual assets to cultivate market stability and security. In response to the shifting geopolitical and business climates, actively support or invest in local research and development of regulatory technology (RegTech). Allocate resources toward intelligent regulatory tools that empower financial regulators to adeptly navigate digital financial risks, thereby safeguarding the interests of consumers and investors alike.
- Bolstering Support for VASPs and VATPs: Amplify assistance for Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) and Virtual Asset Trading Platforms (VATPs), focusing particularly on local legal and tax advisory services, along with tailored incentives to foster growth and compliance.
- Fostering Collaborative Synergies: Stimulate collaboration between financial institutions and tech innovators, paving the way for a seamless fusion of digital technology within traditional financial services, thus enhancing user experience and operational efficiency.
- Certification and Oversight of Virtual Asset Offerings: Advocate for the rigorous certification and regulation of virtual asset-related products, including cryptocurrency exchanges and virtual asset funds. Provide direct support to local regulatory authorities with resources—such as skilled personnel—to expedite and refine the review and licensing processes.
- Cultivating a Digital Finance Ecosystem: Enhance the visibility and appeal of the digital finance ecosystem by funding international FinTech summits, thereby drawing global digital finance companies and investors' attention to Hong Kong's burgeoning market.
- Establishment of a Digital Finance Demonstration Zone: Create a dedicated digital finance demonstration zone in Hong Kong, showcasing physical pilot operations for digital banks and virtual asset exchanges, thus serving as a beacon for innovation and experimentation in the realm of digital finance.
3. Expanding the Utilization of Digital Renminbi (e-RMB)
- Advancing Pilot Initiatives: Propel the initiation and practical application of the digital renminbi in Hong Kong, focusing on pivotal sectors such as financial securities, retail transactions, and cross-border payments. These pilot programs aim to showcase the versatility and efficiency of e-RMB in everyday financial interactions.
- Deepening Collaboration with Mainland China: Fortify partnerships with Mainland China to investigate the seamless integration of digital renminbi with Hong Kong's local payment frameworks. This collaborative effort seeks to enhance capital mobility throughout the Greater Bay Area, creating a more interconnected financial ecosystem.
- Fostering Regulatory Alignment: Advocate for synchronized efforts with Mainland authorities regarding digital financial regulation, data privacy, and technical standards. This coordination is essential for streamlining the integration of digital finance within the Greater Bay Area, ensuring a cohesive approach to digital currency implementation and governance.
4. Accelerating the Development of Digital Hong Kong Dollar (e-HKD)
Hong Kong should leverage its status as an international financial center to accelerate the development of e-HKD, establishing it as a model for global central bank digital currencies (CBDC) and further enhancing financial competitiveness. Ensuring its security, usability, and broad acceptance involves a multifaceted approach that includes technological innovation, policy support, and public participation. Specific measures are recommended as follows:
Technological Innovation
- Pilot Programs: Implement small-scale pilot programs to test the technical feasibility and application scenarios of e-HKD, including retail payments, cross-border payments, and financial transactions.
- Involvement of FinTech Firms: Engage FinTech companies to foster the development of innovative solutions.
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): Introduce DLT and explore the use of blockchain technology to enhance transaction transparency, security, and efficiency. Test a multi-layer architecture where the central bank controls the core system while commercial banks or payment institutions operate the second layer network to ensure efficiency and scalability.
- Upgrade Digital Payment Infrastructure: Strengthen and upgrade digital payment infrastructure to support the high-frequency trading and low-latency requirements of e-HKD. Ensure seamless integration of e-HKD with existing payment systems (e.g., PayMe, Alipay, WeChat Pay, BOC Pay, and Faster Payment System).
- Enhance Cybersecurity: Invest resources in researching quantum-resistant encryption technologies to safeguard against future cyber threats. Establish comprehensive monitoring and emergency mechanisms to protect transaction data security and privacy.
Infrastructure Development
- Efficient Payment Ecosystem: Build an efficient payment ecosystem that includes developing payment terminals and applications supporting e-HKD, ensuring widespread adoption in retail payment scenarios, and advancing the digitization of cross-border payment and settlement systems to enhance Hong Kong's status as an international financial center.
- Cross-Border Applications: Promote cross-border applications by strengthening cooperation with Mainland China, piloting interoperability between e-HKD and the Digital Renminbi, and exploring cross-border payment collaborations with other countries' CBDCs to reduce currency exchange costs and time.
- Enhancing Financial Inclusion: Utilize e-HKD to lower the cost of electronic payments for merchants and individuals, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises and vulnerable groups. Provide user-friendly digital wallets to facilitate wider access to and use of e-HKD.
Policy Measures
- Clear Legal Framework: Develop a clear legal framework and regulatory system governing the use of e-HKD, covering anti-money laundering (AML), combating the financing of terrorism (CFT), and user privacy protection. Clarify the relationship between e-HKD and existing monetary policies to ensure no negative impact on financial stability.
- Alignment with International Standards: Align with international standards by referencing the development experiences of other CBDCs (e.g., China’s Digital Renminbi, European Central Bank’s Digital Euro). Participate in discussions and research on CBDCs led by international financial institutions (e.g., IMF, BIS) to ensure e-HKD meets global standards and can circulate as an international currency.
Public Participation
- Education and Outreach: Educate the public on the usage and advantages of e-HKD, such as transaction convenience, security, and privacy protection. Address public concerns regarding digital currencies, especially regarding personal privacy and financial stability.
- User Participation in Trials: Encourage user participation in pilot programs by offering economic incentives, such as cash rebates or discounts, to attract users to engage with e-HKD trials. Collect feedback from users to improve the experience.
- Transparent Communication Mechanism: Regularly update the public on the development progress of e-HKD to strengthen trust and support. Publicly disclose technical audits and pilot results to demonstrate the safety and reliability of e-HKD.
Timeline for Implementation
- Short-Term Goals (1-2 years): Complete technical testing and regulatory framework design.
- Medium-Term Goals (3-5 years): Achieve large-scale pilot applications.
- Long-Term Goals (5 years and beyond): Fully promote e-HKD to become a mainstream payment method.
To oversee the implementation process, it is recommended to establish a supervisory committee composed of government representatives, financial institutions, and experts responsible for monitoring the development progress and evaluating the effectiveness of e-HKD implementation. The expert group should comprise practitioners with hands-on experience rather than theoretical academics.
5. Attracting Global Digital Finance Enterprises and Talent
- Strategic Tax Incentives and Financial Support: Implement attractive tax incentives and financial subsidies designed to lure international digital finance firms to set up their headquarters or operational bases in Hong Kong. These incentives will serve as a catalyst for fostering a vibrant financial ecosystem.
- Streamlined Visa Processes: Enhance visa facilitation measures to draw elite technology and digital finance professionals from across the globe. By simplifying the immigration process, Hong Kong can effectively harness these talents to nurture and develop a robust pool of local expertise that meets international standards.
- Creation of Specialized Funds: Establish dedicated funds aimed at supporting the synergistic growth of local startups alongside foreign enterprises. This initiative will promote innovation within the financial technology sector, fostering a collaborative environment that drives cutting-edge advancements and enhances the overall digital finance landscape.
6. Promoting Green Digital Finance
- Incentivizing Financial Institutions: Inspire financial institutions to harness digital technologies for the creation and delivery of green finance solutions. For example:
- Innovative Green FinTech Solutions: Champion the development of environmentally friendly financial solutions powered by cutting-edge technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data. These innovations will enhance both the transparency and efficacy of green financial products, making them more appealing to investors.
- Creation of an Open Green Data Platform: Establish a comprehensive green data platform that prioritizes accessibility for local businesses, offering free access to vital information. This platform should consolidate environmental data, carbon emissions statistics, and corporate sustainability metrics, thereby facilitating informed decision-making.
- Facilitation of Blockchain Applications: Leverage blockchain technology to meticulously track the utilization of green assets, ensuring that allocated funds are directed toward projects adhering to stringent green standards. This transparency will significantly bolster investor confidence.
- Digital Evolution of Green Bonds and Financial Instruments: Promote the digital transformation of the green bond market and other sustainable financial assets to foster a landscape of sustainable finance. Digitizing green financial products is anticipated to yield substantial benefits, outweighing potential drawbacks. By employing blockchain platforms for green bond issuance, transaction costs can be reduced and efficiency enhanced. Furthermore, automating the certification process for green bonds through digital means will improve transparency and expedite issuance. A dedicated digital green bond platform will attract a broader spectrum of international investors to engage with Hong Kong's green finance market, thus channeling significant global capital into sustainable initiatives.
7. Strengthening Cybersecurity and Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
- Subsidizing Advanced Regulatory Solutions: While enforcing the adoption of compliant and secure regulatory tools, consider implementing subsidies or funding programs aimed specifically at financial institutions—particularly small and medium-sized enterprises—to facilitate their transition to cutting-edge regulatory technologies. This support will enable them to enhance compliance without incurring prohibitive costs.
- Cultivating Public-Private Partnerships: Encourage the formation of strategic alliances between public and private sectors to host regular summits and seminars centered on cybersecurity and regulatory technology. Such collaborations will not only attract funding and technological advancements to tech parks and high-tech development zones but will also provide local developers with opportunities to acquire expertise and knowledge from international sources.
- Promoting a Risk-Based Cybersecurity Framework: Advocate for financial institutions to implement a risk-based approach to cybersecurity, tailored to their specific capabilities and challenges. Provide assistance in crafting specialized cybersecurity strategies that address the distinct demands of the financial sector, encompassing areas such as risk assessment, vulnerability management, and incident response protocols.
- Government-Driven Cybersecurity Infrastructure Investment: The government should spearhead investments aimed at bolstering cybersecurity infrastructure within the digital finance realm, ensuring the integrity and security of digital transactions. Additionally, promoting the use of local cybersecurity tools and management solutions will foster a mutually beneficial profit-sharing ecosystem between public and private entities, reinforcing the overall resilience of the financial sector.
8. Education and Public Engagement
- Investing in Financial Literacy Resources: Dedicate increased resources to advance education in financial technology and digital finance. For instance, enhance outreach initiatives on platforms like “The Chin Family in the Investor and Financial Education Council’s,” aiming to deepen public comprehension and acceptance of digital payments, virtual assets, and cybersecurity measures. Moreover, motivate platforms and financial institutions to deliver relevant knowledge and training to the community, fostering a more informed citizenry.
- Collaborative Efforts with Academic Institutions: Forge partnerships with educational establishments to expand the curriculum around digital finance, thereby nurturing local talent in this burgeoning sector. Such collaboration will ensure that students are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to thrive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
- Engaging Industry Experts: Encourage local universities and colleges to invite seasoned industry professionals to share their insights through case studies and practical solutions. This engagement will enrich the academic experience for students and better prepare them for successful careers in the digital finance arena, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application.
Regarding to ESG
A Green Finance Revolution
In the bustling metropolis of Hong Kong, a mere 1% of electricity generation emanates from renewable sources. This startling statistic, sourced from the Hong Kong Energy Statistics Annual Report 2022, paints a picture of dependency on imported power—nuclear energy accounts for a substantial 28%, while the lion's share, 48%, thrives on natural gas. Meanwhile, across the globe, other financial hubs are outpacing Hong Kong in the renewable race. London's energy landscape is electrified with a 40% contribution from renewables, as highlighted in the UK Department of Energy 2023 Report. Across the Atlantic, New York strides forward with a commendable 20% as per the U.S. Energy Information Administration 2023 Report. Even Singapore, a city-state bathed in sunlight, is harnessing solar power to reach 4% of its energy production, according to the Energy Market Authority of Singapore 2023.
The message is clear: Hong Kong must sprint, not saunter, towards a greener future. The challenge? Achieving monumental advancements with prudent financial strategies. But fear not, for we have a blueprint, a roadmap, a vision. Specific yet strategic, our recommendations are poised to transform Hong Kong’s energy tapestry, weaving in threads of sustainability, innovation, and resilience. It's time to turn the tide, to light up the city with the power of the sun, the wind, and the waves. The journey begins now, for tomorrow's energy is in our hands today.
Strategic Recommendations for Advancing Hong Kong's Renewable Energy Landscape
1. Implement a Robust Long-term PPA Support Mechanism
To catalyze the growth of new energy projects, establishing long-term Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) is imperative. These agreements serve as a beacon of revenue stability, enticing private capital investment into the burgeoning field of renewable energy.
- Proposed Pricing Framework: Hong Kong should consider aligning its PPA pricing with international benchmarks, such as those in the UK and New York. A competitive rate of 1.2 HKD per kWh, translating to approximately 1,200 HKD per megawatt-hour, is recommended.
- Global Insights:
- The UK's 2023 Contracts for Difference (CfD) auction set an average PPA price for offshore wind at 500 HKD per megawatt-hour, approximately £50.
- In New York State, the offshore wind PPA price hovers around 650 HKD per megawatt-hour, roughly $83.
- Revenue Aspirations: Consider a 1 GW offshore wind project. Such an endeavor could yield an impressive 2.6 billion kWh annually, securing investors a stable revenue stream of 3.1 billion HKD. This initiative would significantly bolster Hong Kong's renewable energy quotient, steering the city towards a future where clean energy isn't merely an option but a standard.
2. Introduce Targeted Tax Incentives
To spur investment in Hong Kong's new energy sector, strategic tax incentives are essential. These measures should be tailored to enhance the financial appeal and viability of renewable energy projects.
- Profits Tax Exemption: Implement a 10-year profits tax exemption for projects focused on wind, photovoltaic, and energy storage systems. This initiative aims to amplify investment returns and attract more stakeholders to the renewable energy space.
- Streamlined Import Procedures: While Hong Kong already offers exemptions on most import duties, further simplification of import procedures is crucial. By reducing logistics time and associated costs, the importation of new energy equipment can be expedited, facilitating quicker project deployments.
- Global Comparisons:
- In Singapore, corporate income tax exemptions range from 5 to 15 years, as highlighted by the Energy Market Authority of Singapore 2023.
- Vietnam offers a 13-year tax rate reduction specifically for new energy projects, according to the PwC Vietnam Tax Handbook 2024.
These incentives not only align Hong Kong with international best practices but also position it as a competitive player in the global renewable energy arena.
3. Incentives for Land and Offshore Area Usage
To facilitate the growth of offshore wind and photovoltaic power projects, providing advantageous land and sea area usage rights is crucial. This approach would enable the development of substantial renewable energy infrastructure in strategic locations.
- Proposed Locations and Capacities:
- Southeastern Waters of Hong Kong: Ideal for establishing a 1,000 MW offshore wind farm, this area has the potential to generate approximately 2.6 billion kWh annually.
- Dapeng Bay: This location can support a 500 MW wind farm, contributing significantly to the region's renewable energy output.
- Southern Waters of Lamma Island: With the capacity for a 300 MW wind farm, this area offers further opportunities for renewable energy expansion.
- Global Benchmark:
- In the Netherlands, the government provides free usage rights for offshore wind farms in the North Sea, according to the Netherlands Renewable Energy Association 2023.
By offering these incentives, Hong Kong can attract significant investments and expertise, aligning its renewable energy strategies with successful international models. This initiative would not only enhance energy security but also cement Hong Kong's status as a leader in sustainable development.
4. Support for Shared Cable Construction Costs
Offshore wind projects necessitate the installation of submarine cables to integrate with the grid, which represents a significant portion of the total investment—approximately 15% to 20%.
- Recommendation: To reduce the financial barrier for investors, the government could subsidize 30% to 50% of the cable construction costs. This support would effectively lower the initial investment threshold, making these projects more financially feasible.
- Global Insight:
- European North Sea wind farms have demonstrated that governmental funding for grid infrastructure can significantly boost private investment, as noted in the International Energy Agency 2023 Report.
By adopting this approach, Hong Kong can stimulate private sector involvement in offshore wind projects, fostering innovation and accelerating the transition to renewable energy. This collaborative model would enhance the city's energy infrastructure while promoting sustainable economic growth.
5. Expand Green Bonds and Bank Loans
To further propel the growth of renewable energy projects in Hong Kong, an expansion of the Hong Kong Green Bond Program, along with the introduction of dedicated low-interest green loans, is recommended.
- Funding Objectives: These financial instruments should be directed towards the development of wind power, photovoltaic power generation, and energy storage infrastructure. By doing so, they will provide the necessary capital to drive innovation and expand the city's clean energy capabilities.
- Global Benchmarks:
- In 2023, Singapore issued green bonds amounting to USD 3.5 billion, as reported by the Government of Singapore.
- The European Investment Bank consistently provides around EUR 5 billion annually in green loans to support infrastructure development, according to their 2023 Report.
By following these international examples, Hong Kong can significantly enhance its renewable energy financing mechanisms. This strategic expansion will not only attract more investors but also ensure that Hong Kong remains at the forefront of sustainable finance and development.
6. Establish a Green Infrastructure Fund
The creation of a Green Infrastructure Fund is essential for supporting local renewable energy projects and attracting international investment into Hong Kong's new energy sector.
- Background and Necessity:
- Currently, Hong Kong lacks a cohesive green infrastructure funding platform, which restricts the financial integration and scalability of new energy initiatives.
- By establishing a Green Infrastructure Fund, Hong Kong can alleviate early-stage funding pressures and draw in substantial private capital, thereby enhancing project viability and sustainability.
- Successful Global Models:
- UK Green Investment Bank (GIB): With an initial funding pool of £3 billion (approximately HKD 30 billion), the GIB successfully attracted private capital amounting to three times its initial investment, illustrating the power of leveraging public funds to catalyze private sector participation.
- Singapore Green Infrastructure Fund: With an initial scale of USD 2 billion (approximately HKD 15.6 billion), this fund is dedicated to advancing solar and energy storage projects across the Asia-Pacific region, showcasing a focused approach to regional clean energy advancement.
By adopting a similar strategy, Hong Kong can create a robust financial ecosystem that not only supports local renewable projects but also positions the city as a key player in the global green finance landscape. This fund would act as a magnet for international investors, fostering innovation and sustainable development within the region.
7. Establish a Dedicated Department and Set KPIs
Creating a specialized department focused on new energy development is crucial for coordinating efforts and achieving strategic energy goals in Hong Kong.
- Objectives:
- Renewable Energy Target: Aim to increase the proportion of renewable energy in Hong Kong to 15% by 2035.
- Offshore Wind Capacity: Develop and achieve an installed capacity of 3 GW in offshore wind power by the same year.
- International Benchmark:
- The UK's National Infrastructure Commission (NIC) serves as a model, with its annual energy progress reports that drive policy implementation and accountability.
By establishing this dedicated department, Hong Kong can ensure focused oversight and efficient management of renewable energy projects. Setting clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) will guide progress, facilitate transparency, and ensure that the city meets its ambitious energy targets. This strategic move will align Hong Kong with global best practices in energy governance and policy execution.
8. Simplify Project Approval Process
To enhance the efficiency of new energy project deployments in Hong Kong, it is crucial to streamline the approval process, reducing the timeline from the current 36-48 months to 12-18 months. This can be achieved by adopting best practices from Mainland China, which are known for their efficiency in project approvals.
Policy Benefits:
1. Support for Achieving the 15% New Energy Target:
- By expediting the approval process, offshore wind, photovoltaic, and energy storage projects can collectively contribute an additional 2 GW of renewable energy capacity annually. This acceleration will play a significant role in reducing carbon emissions and reaching Hong Kong's renewable energy goals.
2. Promotion of Green Finance:
- Establishing a Green Infrastructure Fund and expanding the green bond program can attract substantial international capital to Hong Kong.
- By fostering collaboration with global institutions such as the Asian Development Bank and the European Investment Bank, Hong Kong can position itself as a leading green finance hub within the Asia-Pacific region.
3. No Increased Fiscal Pressure:
- The strategy recommends leveraging market mechanisms, with the government providing essential policy support and initial funding. This approach encourages the involvement of private capital, thereby reducing the fiscal burden on public finances.
By simplifying the project approval process and implementing these strategic benefits, Hong Kong can accelerate its transition to a more sustainable energy future, all while maintaining fiscal responsibility and enhancing its status as a green finance leader.
Sum Up
The advancement of new energy technologies stands as a pivotal cornerstone for Hong Kong's ambitious energy transformation. This shift is not merely a regulatory formality; it is a strategic maneuver that can significantly bolster the region's standing in the realm of green finance. Imagine the potential unleashed by the establishment of a robust green infrastructure fund! Coupled with enhanced policy support mechanisms and a simplification of approval processes, these initiatives could dramatically elevate the share of renewable energy sources in Hong Kong's energy mix.
As the city positions itself as a beacon of international green finance, the implications are profound. The journey towards long-term sustainable development is fraught with challenges, yet the rewards—both environmental and economic—are undeniably compelling. In this dynamic landscape, innovation and adaptability will be crucial, paving the way for a greener, more resilient future.
Conclusion:
As Hong Kong charts its fiscal path for the 2025-26 period, the city stands at a crossroads that requires strategic foresight and decisive action. The examination of its fiscal policies reveals underlying vulnerabilities tied to a narrow revenue base and persistent structural deficits. Addressing these challenges necessitates a multifaceted approach, focusing on diversifying revenue sources and implementing sustainable fiscal policies. The government must prioritize long-term planning and innovative financial strategies to stabilize and strengthen Hong Kong's economic foundation.
By expanding the tax base and refining expenditure management, Hong Kong can mitigate the risks associated with its current fiscal structure. Moreover, embracing transparency and responsible fiscal governance will be crucial in maintaining the city's esteemed status as a global financial hub while safeguarding the welfare of its citizens. As the government prepares to unveil the new budget, it is essential to incorporate insights from diverse stakeholders, fostering a collaborative effort to drive economic development and implement practical, future-oriented solutions. In doing so, Hong Kong can secure a resilient economic future, poised to thrive amidst global uncertainties.
If you have any inquiries regarding this letter, please feel free to contact me or Mr. LIU Tsan Pui Martin, the Director of the Industrial Relations Department.
Your Sincerely,
Mofiz Chan
Chairman
Hong Kong Securities and Futures Professionals Association
The shadow of economic prospects
In the coming years, the challenges confronting the Hong Kong government will extend well beyond mere fiscal deficits, encompassing a spectrum of issues such as decelerating economic growth, an aging populace, and the unpredictable nature of the global economic environment. Should Hong Kong's economy and real estate sector continue to stagnate, we may face a protracted fiscal deficit that could ultimately precipitate a crisis of resource depletion. Although current fiscal reserves may appear sufficient, their sustainability is likely to be rigorously tested as deficits escalate, raising significant concerns regarding future economic viability.
While the fiscal framework of the Hong Kong government may outwardly project a strong economic foundation, it conceals critical vulnerabilities tied to structural deficits and various economic challenges. A lack of proactive management in terms of revenue generation and expenditure has stymied effective diversification of income sources, thereby posing substantial risks to fiscal sustainability. In this uncertain economic landscape, the financial resilience of the Hong Kong government will face formidable challenges. It is only through transparent and responsible fiscal governance that Hong Kong can hope to preserve its esteemed status as a global financial hub and protect the welfare of its citizens moving forward.
As the budget proposal draws near, we earnestly hope that the government will thoughtfully consider the perspectives of diverse stakeholders, including this council. In a spirit of patriotism and unwavering dedication to Hong Kong, we aim to collaborate on fostering economic development and crafting practical solutions for the future.
Recommendation for the Government to Guarantee Bond Issuance to Facilitate Financing for SMEs
In the context of ongoing global economic instability, small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in Hong Kong are grappling with significant financing challenges. These enterprises serve as vital pillars of the local economy, contributing greatly to innovation and employment. Despite their importance, many SMEs are encountering substantial obstacles in securing the financial support they require, particularly as banks tighten their lending standards during economic downturns—a situation aptly described by the adage “closing umbrellas when it rains.”
To alleviate these financing difficulties, we strongly recommend that the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government take proactive measures to facilitate the issuance of bonds. This initiative should be supported by local chambers of commerce and Hong Kong chambers located across various regions of Mainland China, thereby providing SMEs with more reliable and stable financing channels.
Data from the Hong Kong Monetary Authority reveals a tentative improvement in the financing landscape during the first quarter of 2024; however, the approval rates for bank loans remain challenging. Many enterprises continue to struggle with the loan application process. Concurrently, the Hong Kong best lending rate has decreased from 5.88% at the end of July 2023 to 5.38% in November 2024, which creates a favorable market environment for bond issuance.
By guaranteeing bond issuance for SMEs, the government can enhance access to capital, fostering a more resilient economic landscape that empowers these vital enterprises to thrive even in uncertain times. This strategic move would not only bolster the financial stability of SMEs but also promote broader economic growth throughout Hong Kong.
Proposed Plan
1. Recommendation for Chambers of Commerce to Participate in Bond Issuance Guaranteed by the HKSAR Government:
- Collaboration and Guarantee: We propose that the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government guarantees the issuance of specialized bonds and actively collaborates with chambers of commerce to encourage their members and SMEs in Hong Kong to participate. This initiative aims to specifically assist capable SMEs that have faced significant challenges in recent years, thereby enhancing their capacity to secure financing while simultaneously reducing their overall cost of capital.
- Use of Funds: The proceeds from these bonds should be strategically allocated to support the business expansion of SMEs across several critical areas, including international trade, global supply chain services, technological innovation, green transformation, and digital upgrades. By channeling funds into these sectors, we can not only bolster the growth potential of SMEs but also contribute to the broader economic development of Hong Kong in a sustainable manner.
This proposed plan stands to fortify the financial resilience of SMEs, ensuring they remain integral contributors to Hong Kong's economic landscape while navigating the complexities of a challenging global environment.
2. Attracting Participation from Private Equity Funds and Consortiums:
- Involvement of Private Equity Funds: We recommend that private equity funds establish dedicated consortiums to engage in this initiative. These consortiums can offer flexible funding solutions along with professional management expertise, enabling SMEs to utilize the raised funds more effectively. By leveraging the resources and networks of private equity funds, SMEs can access not only financial support but also strategic guidance that can enhance their operational efficiency and growth potential.
- Investment Opportunities: The plan aims to attract private equity funds and consortiums by presenting competitive investment returns. While the associated risks may be elevated, the implementation of appropriate asset allocation and risk management mechanisms can effectively safeguard the interests of investors. By clearly outlining the potential for returns alongside robust risk mitigation strategies, we can create an appealing proposition for private equity involvement, ultimately fostering a collaborative environment that benefits both investors and SMEs.
3. Funding Application and Distribution Mechanism:
- Chamber Channels: Member enterprises of the chambers of commerce should be allowed to submit funding applications through their respective chambers. This process would involve preliminary reviews and recommendations by the chambers, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of fund distribution. By leveraging the existing networks and knowledge of the chambers, the government can ensure that funding is directed toward the most viable and deserving SMEs.
- Government-Managed Application Channel: To ensure inclusivity, a government-managed application channel should be established for SMEs that are not members of any chamber of commerce. This channel will provide all eligible enterprises with equal access to funding opportunities, ensuring that no deserving SME is left out of the financing framework.
- Supporting the Future Development Engine of Hong Kong through Healthy Growth of SMEs: To encourage responsible borrowing and timely repayments, funds can be prioritized and offered at preferential interest rates to SMEs that have demonstrated a consistent record of timely repayments over the past five years. This approach not only supports their cash flow but also incentivizes good financial practices, contributing to the overall stability and growth of the SME sector.
4. Policy Support and Transparent Regulation:
- Policy Assurance: The government should provide essential legal and policy support to facilitate the compliant issuance of bonds. This should include offering tax incentives and administrative conveniences that promote ease of access for SMEs to participate in the bond issuance process. Such measures will not only incentivize SMEs to engage with the funding initiative but will also ensure that the funds are utilized effectively and in alignment with regulatory requirements.
- Transparent Regulation: It is crucial to establish a public and transparent oversight mechanism that regularly reports to the public on the initiative's progress and the utilization of funds. This transparency will enhance trust among all stakeholders, including investors, SMEs, and the general public, fostering a collaborative environment that encourages participation and accountability.
By guaranteeing the issuance of bonds and attracting private equity funds to form consortiums, the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region Government can create a stable and flexible financing environment for SMEs. This approach will empower these enterprises to navigate economic challenges and pursue sustainable development effectively. Moreover, this initiative will not only bolster the competitiveness of SMEs but also contribute to the overall recovery and growth of Hong Kong's economy.
We urge the government to thoroughly assess the feasibility of this proposal and collaborate closely with chambers of commerce and financial institutions to ensure the effective implementation of the plan. Together, we can foster a resilient economic landscape that supports the vital role of SMEs in driving Hong Kong's future prosperity.
Strategic Analysis and Detailed Proposal for the Hong Kong Government to Fully Acquire Octopus Holdings Limited
In the backdrop of rapid global digital economic development, electronic payment has become an indispensable part of modern urban life. As an international financial center, Hong Kong boasts a superior financial infrastructure and an innovative environment. “Octopus” is a pioneer in Hong Kong's electronic payment market, underscoring its importance. This article proposes that the Hong Kong government fully acquire Octopus Holdings Limited and explores its detailed economic benefits, implementation steps, and strategic significance.
Market Position and Valuation of Octopus Holdings Limited
Since its establishment in 1997, Octopus has maintained a leading position in Hong Kong's electronic payment market. By the end of 2022, Octopus achieved an annual revenue of HKD 1.6718 billion and a net profit of HKD 613.3 million. Its extensive market applications cover public transport, retail, dining, and other service industries, with over 20.7 million cards in circulation. Based on its stable profitability and market advantage, Octopus's valuation can be assessed using the price-to-earnings (P/E) method.
Assuming a P/E ratio of 15, the valuation is calculated as follows:
Valuation=HKD 613.3 million×15=HKD 9.1995 billion
This valuation provides a financial benchmark for the government acquisition.
Acquisition Cost Analysis
The ownership structure of Octopus is complex, with MTR Corporation holding 86.12% of the shares, and the Hong Kong government holding 75.28% of MTR Corporation, which means the government indirectly holds 64.84% of Octopus. To achieve full acquisition, the government needs to purchase the remaining 35.16% of shares. Based on the valuation of HKD 9.1995 billion, the cost for the government is:
Acquisition Cost=HKD 9.1995 billion×0.3516=HKD 3.233 billion
Deposit Management and Financial Strategy
The deposits charged to commercial users by Octopus are one of its important funding sources. Assuming a deposit of HKD 2,000 per Octopus machine and a total of 46,000 merchants, the total deposits would amount to HKD 920 million. As of 2017, with over 34.5 million Octopus cards in circulation, each card having a deposit of HKD 50, the total deposits collected would amount to HKD 1.725 billion. The total deposit calculation is as follows:
If these deposits are placed in a bank with an annual interest rate of 3.5%, the annual interest income would be:
Interest Income = HKD 2.645 billion × 3.5% = HKD 92.57 million.
This income can be used to subsidize Octopus's operational costs and further support the development of electronic payment infrastructure.
Promoting Digital Hong Kong Dollar and E-currency Adoption
Following the full acquisition of Octopus, the government could seamlessly integrate its payment platform with the “Digital Hong Kong Dollar,” significantly enhancing the adoption of digital currency. In 2024, Octopus began waiving the transaction fee for the first HKD 10,000 of monthly transactions for merchants using the business version of the app. This policy benefits over 80% of merchants by significantly reducing transaction costs for small and medium enterprises.
Additionally, more than 25,000 taxi drivers have installed the commercial version of the Octopus app, providing a solid foundation for digital currency application in the transportation sector. Promoting digital currency will reduce cash circulation, lowering cash management costs for merchants and improving operational efficiency.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation Strategies
Despite the significant potential benefits of acquiring Octopus, the government must address the following risks:
1. Market Competition Pressure: With the rise of other payment platforms, Octopus needs to continually innovate to maintain competitiveness.
2. Technology Upgrade Needs: Electronic payment technology is rapidly evolving, requiring government investment to ensure the Octopus system's advancement and security.
3. Public Reaction: Government intervention in private enterprises may draw public attention, necessitating effective communication and transparent management.
Long-term Benefits and Strategic Significance
Fully acquiring Octopus will not only consolidate Hong Kong's leading position in the electronic payment market but also drive the digital transformation of society as a whole. By lowering transaction costs and enhancing payment efficiency, Hong Kong's SMEs will become more competitive in the global market. This move aligns with the government's long-term strategy to promote digital economic development, laying a solid foundation for Hong Kong's sustainable economic growth.
Conclusion
The Hong Kong government's full acquisition of Octopus Holdings Limited is a strategic decision with far-reaching impacts. By integrating resources and guiding policy, the government can promote the widespread adoption of digital currency while supporting SME development and enhancing Hong Kong's international competitiveness. This initiative will not only bring significant economic benefits to Hong Kong but also foster the digital transformation of society, fueling future economic growth.
Strategies for Improving Hong Kong's Financial Market: Drawing Inspiration from the U.S. Experience
Introduction
As an international financial center, Hong Kong must continuously strive to maintain its competitiveness and adapt to the evolving dynamics of the global market. To achieve this goal, it is essential to analyze the differences between Hong Kong and the United States in key areas such as exchange diversity, financial market access, margin requirements, listing thresholds, regulatory oversight of fiscal resources, and anti-money laundering standards. By leveraging the successful experiences of the U.S., Hong Kong can optimize its financial market structure and regulatory framework, ultimately enhancing its global standing.
Promoting a Diverse Exchange Markets
Currently, Hong Kong relies on a single securities exchange, which to some extent limits market competition and vibrancy. The United States boasts up to 13 exchanges, including the New York Stock Exchange and NASDAQ, and this diversified structure encourages market competition and innovation. If Hong Kong can introduce more exchanges, it would not only reduce trading costs but also attract more international capital inflows, further consolidating its position as a global financial center.
Implementing a multi-exchange system would provide investors with more choices and enhance liquidity, creating a more dynamic trading environment. Additionally, it could foster niche markets for specific sectors, thus promoting broader economic growth and diversification.
Enhancing Flexibility in Market Access
The entry requirements of the U.S. financial markets, particularly regarding technological capabilities and financial health, provide companies with an efficient and transparent environment. In contrast, while Hong Kong's requirements for local knowledge and ongoing professional training ensure a high standard of professionalism, they may also hinder the entry of international enterprises.
To address this, Hong Kong should consider increasing the flexibility of its market access while maintaining professional standards. This could involve streamlining the application processes, offering alternative pathways for compliance, and recognizing international qualifications. By doing so, Hong Kong can attract a wider range of international participants, fostering a more diverse and competitive market landscape. This approach would not only enhance the city's appeal as a financial hub but also stimulate innovation and collaboration across borders.
Enhancing Margin and Risk Management Practices
When it comes to margin and risk management, the United States stands out with its intricate regulations that offer precise guidance to the market. In contrast, Hong Kong's streamlined requirements cater primarily to newcomers, providing an accessible entry point. However, there lies an opportunity for growth. By adopting more advanced risk management frameworks and drawing inspiration from the methodical approach to margin ratios utilized in the U.S., Hong Kong could significantly bolster market transparency and stability. This strategic evolution would not only refine existing practices but also empower investors with a deeper understanding of risk, ultimately fostering a more robust financial ecosystem.
Revising Listing Thresholds to Foster Innovation
The U.S. market's low threshold policy for startups creates an inviting landscape for innovative enterprises, offering them the freedom to flourish. In stark contrast, Hong Kong's current listing requirements—especially those centered on profitability—pose significant barriers that could stifle the growth of pioneering firms. To ignite a wave of innovation, Hong Kong ought to contemplate a recalibration of its listing thresholds, particularly for select industries. Such a move would not only draw in a greater number of inventive companies but also enrich the market’s competitiveness and diversity, ultimately positioning Hong Kong as a vibrant hub for groundbreaking ideas and ventures.
Fortifying Financial Resource Regulation
The FINRA framework in the United States exemplifies a remarkable flexibility in adjusting capital requirements tailored to diverse circumstances, presenting a valuable reference for Hong Kong. As it seeks to uphold market stability, Hong Kong stands at a crossroads where it can delve into more dynamic capital regulation strategies—strategies that are responsive to the unique needs of various financial institutions. By embracing this adaptability, Hong Kong could not only reinforce its regulatory framework but also cultivate a more resilient and versatile market landscape, effectively positioning itself in the global financial arena.
Streamlining Compliance Mechanisms for Greater Efficiency
In the bustling landscape of Hong Kong, where anti-money laundering regulations loom large and stringent, the intricate web of compliance requirements can often weigh heavily on businesses. The United States, conversely, adopts a procedural compliance model that presents a more navigable framework, easing the burdens on enterprises. To bolster its international allure, Hong Kong ought to consider a strategic simplification of select processes, all while steadfastly upholding its rigorous compliance standards. This endeavor could significantly alleviate the compliance costs that businesses currently grapple with, paving the way for a more vibrant and accessible market environment.
Conclusion
To maintain its esteemed stature in the global financial arena, Hong Kong must embrace a relentless pursuit of reform and innovation. By scrutinizing the market structures and regulatory practices of the United States, Hong Kong stands to significantly elevate its financial system, invigorating market dynamism and amplifying international competitiveness. This proactive approach is essential; only by adapting to the evolving landscape can Hong Kong sustain its pivotal role amidst the swift currents of global finance. In doing so, it will cultivate a more transparent and efficient market environment, ultimately benefiting investors and businesses alike, and ensuring its relevance in an ever-changing world.
Private Equity and Venture Capital Funds
As a pivotal financial center in Asia, Hong Kong has long been a magnet for international private equity (PE) and venture capital (VC) funds, thriving within its well-established financial system and steadfast rule of law. The presence of these funds not only catalyzes local economic growth and job creation but also solidifies Hong Kong's role as a vital conduit, linking global capital to the burgeoning Asian markets. Yet, as the market environment evolves and global economic fluctuations persist, Hong Kong's PE and VC funds now confront a myriad of challenges.
A recent report by PwC highlights a notable deceleration in the growth of Hong Kong's private equity market from 2022 to 2023, particularly within the venture capital segment. Total investments in this sector plummeted from approximately $8 billion in 2021 to under $5 billion in 2023, marking a staggering decline of 33%. Moreover, early-stage financing for startups has become increasingly arduous, especially when compared to more favorable environments like Singapore. These statistics underscore the significant ramifications of global economic uncertainty and structural shifts within the market, revealing the pressing need for strategic adaptation within Hong Kong's investment landscape.
Global Economic Uncertainty and Its Impact on Market Confidence
The aftermath of the pandemic has cast a long shadow over the global economic landscape, profoundly influencing Hong Kong's investment market. Factors such as the sluggish pace of interest rate reductions and escalating geopolitical tensions have collectively dampened the sentiment among global investors, exerting considerable pressure on fundraising efforts and the return potential of various funds.
Despite the U.S. Federal Reserve's decision to decelerate rate hikes in the latter half of 2023, the prevailing high interest rate environment continues to disrupt global capital flows. This situation poses particular challenges for private equity funds that operate in U.S. dollars, as soaring financing costs emerge as a significant obstacle within the industry. According to the South China Morning Post, many private equity funds encountered substantial difficulties in fundraising during 2023, with Hong Kong's share of total fundraising in the Asia-Pacific region plummeting from approximately 15% in 2021 to below 10% in 2023.
Compounding these challenges are the geopolitical tensions that have further strained the investment climate. The ongoing deterioration of U.S.-China relations has eroded global confidence in the Hong Kong market, directly impacting investors' capital commitments. A study conducted by the China Center for International Economic Exchanges (CCG) revealed that in 2023, more than 30% of multinational funds chose to relocate their capital to Singapore as a strategy to mitigate geopolitical risks. These mounting challenges necessitate a thorough reassessment of Hong Kong's strategy for attracting foreign investment, particularly against the backdrop of an increasingly unstable global economic environment.
Weakness in the Secondary Market Hinders Primary Market Development
In Hong Kong, equity investment funds predominantly target the primary market, seeking returns by investing in unlisted companies and anticipating valuation increases. However, the sluggish performance of the secondary market has reverberated through the primary market, with particularly notable effects on the Pre-IPO fund sector.
The year 2023 marked a significant downturn in IPO activity on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange, reaching levels not seen in nearly a decade. According to Deloitte, total IPO fundraising in Hong Kong for 2023 dwindled to approximately HKD 26 billion, a staggering drop from the peak of HKD 430 billion in 2021. This decline has directly impacted the investment returns of Pre-IPO funds, many of which now face the grim prospect of losses upon exit, leading to a pronounced contraction in Pre-IPO investment scales.
A case in point is the listing of technology companies from mainland China. In recent years, numerous domestic firms have pursued Pre-IPO financing in Hong Kong. Yet, due to the plummeting valuations at the time of listing in 2023—where some tech companies saw their market values dip to less than 50% of their original valuations post-IPO—instances of funds reporting losses upon exit have become increasingly common. A senior executive from a Shenzhen private equity fund remarked to the Economic Daily that enthusiasm for Pre-IPO funds has waned significantly over the past year, prompting some funds to suspend operations and redirect their focus toward other investment opportunities.
This detrimental impact extends beyond Pre-IPO funds, affecting other private equity and venture capital entities as well. As liquidity in the exit market diminishes, a growing number of funds are adopting a wait-and-see approach, further exacerbating overall market liquidity issues and perpetuating a damaging cycle that stifles investment potential across the board.
Regulatory Pressure and Escalating Compliance Costs
The stringent regulatory framework has historically been a hallmark of Hong Kong's financial market, bolstering investor confidence and market integrity. However, as compliance requirements continue to escalate, operational costs for funds are also rising significantly. In 2023, the Hong Kong Securities and Futures Commission (SFC) heightened its scrutiny of private equity funds, particularly regarding cross-border capital flows and anti-money laundering (AML) measures. This shift has compelled fund management companies to invest more resources into their internal control departments to ensure adherence to these regulations.
According to a report by UBS, the annual compliance costs for private equity funds in Hong Kong average 2.5% of total fund assets, notably higher than the 1.2% observed in Singapore. This increased compliance burden not only diminishes Hong Kong's allure as a financial hub but also prompts some funds to contemplate relocating their operations to jurisdictions with lower compliance costs.
In addition to rising compliance expenses, regulatory constraints on merger and acquisition (M&A) transactions have further stifled market vitality. Market participants have expressed concerns that Hong Kong's regulations governing corporate M&A activities are excessively stringent, leading to protracted approval processes that heighten transaction uncertainty and associated costs. This situation often results in many deals failing to meet their deadlines. While such regulations may serve to mitigate risks in the capital markets to some extent, they concurrently suppress capital liquidity and undermine the competitiveness of Hong Kong's market, ultimately hindering its potential for growth and innovation.
Revitalizing Market Vitality
To rejuvenate Hong Kong's private equity and venture capital markets, it is essential for both the government and market participants to implement a comprehensive set of measures aimed at improving the current landscape.
Firstly, enhancing the vitality of the secondary market is paramount. Adjusting stamp duty appropriately can significantly lower overall transaction costs and stimulate market activity. The introduction of increased stamp duty in 2021 serves as a pertinent example; it resulted in a rapid decline in trading volume, underscoring the importance of reducing stamp duty to bolster trading engagement.
Secondly, a moderate relaxation of margin trading policies is a critical initiative worth considering. The tightening of margin trading regulations has considerably constrained the financing capabilities of growth enterprises on the Growth Enterprise Market and smaller mainboard companies, thereby reducing interest in Hong Kong listings among SMEs. Easing these policies could attract more short-term investors into the market and provide companies with additional financing avenues, fostering a gradual recovery of the overall market.
Furthermore, the government's funding policies should embrace greater diversification. For funds targeting emerging industries such as fintech, healthcare, artificial intelligence, and green energy, the introduction of direct financial subsidies or tax incentives could effectively attract global venture capital funds to establish a presence in Hong Kong. Continuous optimization of funding programs will be vital in drawing increased capital inflows, thereby promoting the growth of innovative enterprises.
Hong Kong's private equity and venture capital markets are currently navigating a critical transformation phase. While they face numerous challenges—including global economic uncertainty, a sluggish secondary market, and stringent regulations—these obstacles also offer opportunities for reform and innovation within the capital market.
By enhancing capital market liquidity, optimizing regulatory frameworks, and strengthening governmental support for enterprises, Hong Kong can swiftly reclaim its status as a premier investment hub in Asia. Crises often pave the way for transformation, and the future success of Hong Kong's financial landscape hinges on the collaborative efforts of the government, enterprises, and market participants. Together, they can revitalize Hong Kong's equity investment market and restore its competitiveness on the global capital stage.
Regarding Futures
In a recent annual policy address, the Chief Executive articulated a bold vision: transforming Hong Kong into a premier hub for commodity futures. This ambition resonates deeply within the industry, which eagerly anticipates a comprehensive roadmap from the government—one that delineates supportive policies and robust financial backing in the forthcoming budget.
Delving into the numbers, the average daily trading volume for futures and options during the first eleven months of 2024 reached an impressive 140,000 contracts. This figure marks a notable increase of approximately 16% compared to the same timeframe the previous year. Interestingly, index futures dominate this landscape, accounting for over 80% of all futures trading activity in Hong Kong, while other commodity futures lag behind in engagement.
Consequently, industry stakeholders are fervently hoping that the new budget will usher in a multifaceted approach to bolster the commodity futures market. They are particularly focused on the establishment of supportive policies, enticing tax incentives, and the enhancement of market infrastructure.
Herein lie pivotal recommendations and forward-looking prospects:
1. Tax Incentives for Commodity Futures
To invigorate the commodity futures landscape, the government might contemplate a strategic reduction or even a complete exemption of stamp duty and associated taxes on transactions. This move would effectively lower trading costs, enticing a broader spectrum of market participants and fostering increased engagement within the sector.
Additionally, implementing profit tax incentives could significantly enhance the attractiveness of the market. By offering tax reductions or beneficial schemes for companies involved in commodity futures trading, both local and international players would be encouraged to dive into this burgeoning market. Such initiatives would undoubtedly stimulate trading activity, paving the way for a more dynamic and robust commodity futures environment.
2. Support for Market Infrastructure
To bolster the commodity futures market, the government should contemplate the establishment of a dedicated fintech development fund. This fund would specifically cater to the needs of fintech companies focused on creating innovative trading platforms and technologies tailored for commodity futures. Such an initiative would not only enhance trading efficiency but also fortify security measures within the market.
Moreover, integrating cutting-edge technologies such as blockchain and artificial intelligence can usher in a new era of transaction transparency and operational efficiency. These technologies could facilitate the development of smart contracts, which would streamline trading processes and significantly reduce associated costs.
In tandem with these initiatives, government support for the development of futures exchanges is crucial. By providing targeted funding or policy assistance, existing exchanges could expand their market reach and enhance their operational capabilities. This would result in a broader array of trading options for commodity futures, ultimately heightening market competitiveness and attracting diverse participants.
3. Promotion and Education
To elevate the profile of the commodity futures market, it is imperative that the government, in collaboration with futures exchanges, spearheads a series of educational and promotional initiatives. By organizing seminars, workshops, and informative sessions, they can effectively disseminate crucial knowledge about commodity futures. Such efforts would significantly enhance public awareness and deepen the understanding among market participants regarding the intricacies and opportunities within this sector.
Furthermore, forging partnerships with higher education institutions and vocational organizations is essential. The government should champion the development of specialized professional courses focused on commodity futures. This initiative would not only equip aspiring professionals with the necessary skills but also elevate the overall professional standards within the market. By enhancing the qualifications of industry practitioners, the sector would benefit from a more knowledgeable and capable workforce, ultimately driving growth and innovation in commodity futures trading.
4. Market Diversification
As global markets continue to intertwine, Hong Kong stands poised to emerge as a preeminent futures trading hub in Asia, attracting a diverse array of international investors. To realize this potential, the Hong Kong government and exchanges must amplify their collaboration with other leading financial centers, thereby streamlining the feasibility of cross-border commodity futures trading and delivery mechanisms.
Moreover, in response to the escalating market demand for sustainable and environmentally conscious products, Hong Kong has an opportunity to innovate by developing commodity futures that align with environmental, social, and governance (ESG) criteria. By introducing products from emerging markets—such as carbon credits and sustainable agricultural commodities—Hong Kong can broaden the spectrum of available futures, tapping into a growing niche that prioritizes sustainability.
Additionally, it is vital to provide robust support for Hong Kong's exchanges and financial institutions to participate in international financial exhibitions. Such engagement would not only showcase Hong Kong's capabilities but also bolster its global image as a leading center for commodity futures trading, fostering greater recognition and investment in the region.
5. Regulatory Environment
In light of the swift evolution of fintech and its profound impact on the market, existing regulatory policies have found it challenging to keep pace with these advancements. To address this gap, it is essential for the government, exchanges, and regulatory bodies to adopt a flexible and responsive approach. This involves dynamically adjusting relevant policies in alignment with market developments and emerging demands, ensuring that the regulatory framework remains attuned to the ever-evolving landscape.
Regulatory agencies should proactively revise existing rules to reflect current market dynamics while simultaneously establishing a clear and coherent regulatory framework. This framework must aim to provide a stable and transparent environment that fosters confidence among market participants. Additionally, creating a comprehensive legal structure is crucial for safeguarding the rights and interests of all stakeholders involved. By doing so, the regulatory environment will become more conducive to growth, ultimately enhancing the attractiveness and viability of the commodity futures market.
6. Commodity Warehousing
A compelling proposal envisions the establishment of a dedicated spot commodity delivery site and warehouse on the vacant land at the Kwai Chung Container Terminal. By leveraging the inherent logistics advantages of this prime location and designating it as a bonded area, Hong Kong can significantly enhance its role in the commodity trading landscape. This initiative would not only utilize Hong Kong's robust financial services sector—bolstered by an array of professional financial, legal, and logistics service providers—but also ensure comprehensive support for commodity trading activities.
Moreover, Hong Kong's strategic geographical position at the heart of Asia serves as a catalyst for trade with Mainland China and other neighboring countries. This advantageous location, combined with an established transportation network and sophisticated logistics infrastructure, amplifies the efficiency of goods transportation and distribution across the region.
As a prominent global financial center equipped with a mature financial market, a robust legal framework, and a seamless settlement system, Hong Kong is ideally situated to facilitate financing and settlement processes for commodity trading. The development of dedicated commodity warehousing facilities would pave the way for positioning Hong Kong as a leading hub for commodity futures trading.
In conclusion, if the forthcoming budget can effectively bolster the commodity futures market through these initiatives, it stands to attract a greater influx of both domestic and international investors. This surge in activity would enhance the competitiveness of Hong Kong's commodity futures market, further entrenching its status as a vital financial center. Such strides would not only strengthen market competitiveness but also cultivate a sustainable environment for long-term market development and investment.
Regarding to the Investor Compensation Fund
In recent months, advertisements have proliferated across the vibrant landscapes of Hong Kong, Kowloon, and the New Territories. One particularly striking image features a cheerful pink pig clutching a shield adorned with the character “存,” which translates to “save.” This lively mascot heralds the recent elevation of the bank deposit protection limit to an impressive HKD 800,000. My friend has expressed admiration for the safety of Hong Kong's banks, feeling reassured while engaging in the buying and selling of securities. However, my friend is unaware that Hong Kong also has another financial protection scheme—the Investor Compensation Fund, which specifically safeguards investment matters and offers a higher limit than the bank deposit protection.
The Investor Compensation Fund (hereafter referred to as the Compensation Fund) is under the stewardship of the Securities and Futures Commission and commenced operations alongside the enactment of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571) in 2003. This single fund effectively consolidated three previous compensation schemes: the Stock Exchange Compensation Fund, the Futures Exchange Compensation Fund, and the Dealer Margin Scheme.
The primary objective of the Investor Compensation Fund is to provide a safety net for investors of all nationalities who incur losses due to the misconduct of intermediaries, such as licensed brokers. The compensation limit is set per investor: for those holding securities accounts, the compensation limit stands at HKD 500,000, while a similar cap applies to futures account holders facing broker misconduct. This means that an investor with both securities and futures accounts under the same broker could potentially claim up to HKD 1,000,000, surpassing the bank deposit protection limit.
Moreover, the Compensation Fund extends its coverage beyond just securities and futures contracts traded on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange; it also includes A-shares traded via the Stock Connect scheme. Compensation amounts are determined based on the closing price of the relevant securities or futures contracts at the time of the misconduct. It is crucial to note that misconduct refers specifically to actions such as broker insolvency, bankruptcy, fraud, or embezzlement, rather than market fluctuations or declines.
Investors who have suffered losses and wish to seek compensation can submit their claims to the Investor Compensation Company, which meticulously manages these claims. The application process is clearly outlined on their website, where the Company assesses whether misconduct has occurred and if the claimant qualifies for compensation. If a claimant contests the decision, they may appeal to the Securities and Futures Appeals Tribunal.
Unlike the deposit protection scheme, which sees banks ultimately bearing the costs of compensation, the Compensation Fund is financed primarily through transaction levies imposed on investors during securities or futures trading. This levy system includes a mechanism that allows for the suspension or resumption of levy collection based on the net asset value of the fund. Since 2005, the levy has been suspended, and in 2020, the maximum compensation amount was raised from HKD 150,000 to HKD 500,000 to accommodate significant growth in investor assets and maintain a compensation coverage level of approximately 80%.
The current Securities and Futures Ordinance imposes rigorous oversight on licensed brokers, leading to occasional complaints from industry insiders. Brokers must adhere to stringent financial resource regulations, comprehensive financial reporting requirements, and internal controls, such as disclosing the benefits of sale products and assessing clients’ suitability for investment. Despite challenging market conditions and fierce competition, many brokers have managed to navigate operations smoothly without resorting to the Compensation Fund. In fact, since the Fund established on 2003, with only six claims invitations issued since the fund's inception, illustrating the stability of licensed brokers and the protective role of the fund.
Yet, amid the prominence of the deposit protection scheme, the Investor Compensation Fund remains relatively obscure, leaving many investors unaware of their rights and protections. While it is unlikely that the government intentionally prioritizes one sector over another, the lack of visibility for the Compensation Fund raises questions. Why is there a concentrated effort to promote the deposit protection scheme while the broader protective measures for investors in Hong Kong are overlooked? Why aren’t the benefits of investor protection plans more effectively communicated to strengthen investor confidence and enhance the competitiveness of the market? These pertinent questions warrant careful consideration and action from relevant authorities to bolster investor trust in the landscape of Hong Kong's financial markets.
Sources: Legislative Council documents, Securities and Futures Commission, Investor Compensation Company.
Suggestions regarding listing regulations
1. Enhance the Listing System for Greater Appeal
To draw in a diverse array of high-caliber enterprises, particularly those flourishing in dynamic sectors like hard technology and biotechnology—already thriving on prominent domestic and international exchanges—it's imperative to refine our approach. Imagine the potential of instituting a streamlined dual listing mechanism, designed to entice these innovative companies to actively trade their shares on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. By implementing such strategic initiatives, we can significantly enrich the pool of quality investment opportunities available in the Hong Kong market, ultimately amplifying its allure and competitive edge within the global financial arena.
2. Refine the Investor Landscape in the Hong Kong Stock Market
To invigorate participation from a broader spectrum of qualified mainland investors in the Hong Kong stock market, it is essential to bolster the interconnectivity between these two markets. This could involve fine-tuning the Shanghai-Hong Kong and Shenzhen-Hong Kong Stock Connect mechanisms, making them more user-friendly and efficient. Additionally, lowering the barriers and costs associated with mainland investors' entry into Hong Kong stocks can create a more inviting environment. Such enhancements are poised to catalyze a significant influx of capital into the Hong Kong market, diversify the investor demographic, and ultimately stimulate vibrant market activity that resonates with both local and international stakeholders.
3. Amplify Promotion and Education for the Hong Kong Stock Market Among Investment Institutions
To cultivate a robust influx of long-term value investors—think pension funds and sovereign wealth funds—it's crucial to intensify efforts in promoting the Hong Kong stock market while simultaneously educating both domestic and international investment institutions. By fostering a deeper understanding of the market's unique strengths and potential, we can bolster investor confidence and awareness. Such initiatives will not only stabilize market sentiment and enhance valuations but also establish the Hong Kong stock market as a premier destination for discerning investors seeking sustainable growth and long-term returns. Through strategic outreach and educational programs, we can create a compelling narrative that resonates with these pivotal financial entities, ensuring their ongoing engagement and investment.
4. Enhance Overall Liquidity in the Hong Kong Stock Market
As we approach the conclusion of the U.S. interest rate hike cycle, a unique opportunity arises to invigorate liquidity within the Hong Kong market and elevate valuations. It is essential to implement forward-thinking policies, such as entirely abolishing the stock stamp duty, which would significantly diminish the costs tied to high-frequency trading. This strategic move is anticipated to unleash a wave of trading activity, fostering a more dynamic and vibrant market environment. By capitalizing on these developments, we can not only enhance liquidity but also attract a wider array of participants, ultimately strengthening the overall resilience and appeal of the Hong Kong stock market.
5. Strengthen Cooperation and Communication with International Markets
To bolster the international competitiveness and influence of the Hong Kong market, it is vital to strengthen cooperation and communication with global financial arenas. By actively engaging with key international stakeholders and fostering strategic partnerships, we can create a synergistic effect that enhances the overall appeal of the Hong Kong market. This collective effort has the potential to significantly improve the valuation landscape of the Hong Kong IPO market, paving the way for a resurgence that positions it back at the forefront of global financial hubs. Through these collaborative initiatives, we aim not only to elevate market stature but also to instill renewed confidence among investors, ensuring a robust and dynamic future for Hong Kong's financial ecosystem.
6. Propose a Temporary Reduction in Minimum Market Capitalization Requirements for Main Board Listings
In light of the current sluggish market conditions, where many industries are grappling with low price-to-earnings ratios, the existing stipulations for listing on the Hong Kong Main Board—specifically, the minimum profit requirement of HKD 35 million and the market capitalization threshold of HKD 500 million—may hinder potential applicants. This requirement, reflecting a historical price-to-earnings ratio of 14.3 times, presents a significant barrier, even for those who meet the profit criteria. To invigorate the Hong Kong IPO market, it is advisable to temporarily reassess and reduce the minimum market capitalization requirements for qualifying applicants. By doing so, we can foster a more inclusive environment that encourages new listings and enhances the overall dynamism of the market, ultimately contributing to a more vibrant and competitive financial landscape.
7. Advocate for the Relaxation of Listing Regulations Concerning Newly Injected Assets by Listed Companies
The current framework governing anti-takeover actions delineates specific scenarios—namely, changes in control of a listed company and substantial asset acquisitions aimed at new controlling shareholders or their associates within a 36-month window surrounding such changes. These stringent regulations may inadvertently stifle growth and innovation among listed companies. Therefore, it is prudent to reevaluate the stipulations surrounding anti-takeover measures, particularly by relaxing the listing regulations concerning newly injected assets. Such adjustments could significantly enhance the attractiveness of Hong Kong's listing environment, fostering a more dynamic market that revitalizes the value of listed companies. By encouraging strategic asset injections, we can bolster investor confidence and position Hong Kong as a more appealing destination for corporate growth and investment.
Government Bond Issuance as Revenue
1. Assessment of Bond Issuance Scale and Effectiveness
The scale of bond issuance must be carefully considered, and a thorough evaluation of future repayment capacity is essential before deciding to issue bonds. It is crucial to rigorously assess the effectiveness of debt utilization, ensuring that borrowed funds are directed toward projects that can provide sustainable and stable returns while also delivering significant social and economic benefits. This approach helps avoid investment in unprofitable ventures, which could lead to a debt repayment crisis in the future.
For example, funding in education and technological research and development can effectively enhance the quality of human resources in Hong Kong and improve innovation capabilities, laying a solid foundation for future economic growth. Similarly, investing in infrastructure upgrades, such as transportation, can significantly enhance urban operational efficiency and competitiveness.
Conversely, funds should not be easily allocated to projects lacking clear profit prospects, those with high risks, or initiatives of minimal strategic significance to Hong Kong. Such investments could lead to economic inefficiencies and make future debt repayment challenging, potentially resulting in a debt trap.
2. Enhancing Financial System and Information Transparency
To cultivate a more transparent financial management framework, it is essential to adopt an Accrual Basis for fiscal budget preparation and to establish a routine public reporting mechanism regarding the territory's debt situation. This comprehensive disclosure should encompass intricate details about the scale of the debt, its intended purposes, repayment strategies, and other pertinent information. By elucidating Hong Kong's financial standing in such a manner, we can significantly bolster public confidence and trust in the region's fiscal health.
Furthermore, by stabilizing market expectations through enhanced transparency, we can solidify Hong Kong's reputation within the international financial landscape. Such proactive measures not only foster a sense of accountability but also enhance the credibility of the financial system, ultimately reinforcing the territory's image as a reliable and transparent hub for global investors.
3. Diversifying Revenue Sources and Streamlining Expenditures
The urgent need for comprehensive revenue-generating and cost-saving strategies cannot be overstated. In terms of revenue generation, it is critical to look beyond traditional taxation and bond issuance. Significant efforts should be directed towards fostering the development of new industries through targeted policy support and tax incentives. For example, actively nurturing emerging sectors such as the digital economy and green finance can broaden the high-value-added service industry in Hong Kong, creating new economic growth points and additional sources of taxation.
On the expenditure side, establishing a dedicated team within the auditing department to conduct thorough reviews of government expenditures is recommended. This initiative aims to identify and eliminate unnecessary administrative costs and inefficient investments. By optimizing government operational processes, we can enhance administrative efficiency and reduce the consumption of human and material resources.
Moreover, exploring diversified financing channels is essential for mitigating debt risks. For future large-scale infrastructure projects, reliance on a single bond financing model should be minimized. Instead, actively pursuing public-private partnership models can leverage the strengths of private enterprises in funding, technology, and management expertise, thereby complementing government resources. Additionally, attracting foreign investment for Hong Kong's construction and development is crucial. By formulating favorable policies and creating a conducive investment environment, we can draw in international capital, alleviate funding pressures, and introduce advanced technologies and management practices, ultimately supporting the internationalization of Hong Kong's economy.
4. Industry Expansion and Broadening the Tax Base
As Hong Kong advances in developing its bond market, a proactive strategy is essential for ensuring the sustainable recovery of long-term revenue streams. It is crucial to actively seek effective methods for reasonably broadening the tax base, particularly in response to the significant challenges posed by structural fiscal deficits. Strengthening the unique scale and diversity of Hong Kong's industries has become an urgent priority.
Investing in and supporting sectors such as cultural and creative industries, healthcare, and high-end manufacturing is vital for fostering local brands and enterprises. This will enhance their competitiveness and standing within the global supply chain. By providing policy guidance and integrating resources, the government can facilitate collaborative development across various industries, creating cluster effects that lessen the dependence on traditional sectors like finance and real estate.
By fundamentally solidifying Hong Kong's fiscal revenue base through the establishment of a diversified and sustainable industrial structure and income system, the economy will gain resilience against the complexities of the global economic landscape. This strategic approach will ensure the long-term stability and healthy operation of Hong Kong's economy, positioning it for sustainable growth and prosperity.
Regarding Digital Finance
1. Support the Construction of Digital Financial Infrastructure
Promote the development of Cyberport and Hong Kong Science Park to attract more FinTech companies, including Virtual Asset Trading Platforms (VATP) and various Virtual Asset Service Provider (VASP) firms in Hong Kong. Offering tax incentives can encourage international FinTech companies to establish regional headquarters or research and development centers in the region.
Enhance the application infrastructure for technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data within the financial sector. Optimize Hong Kong's digital payment infrastructure to facilitate the interoperability of cross-border payment systems, particularly in collaboration with mainland China (e.g., the “Cross-Border Wealth Management Connect”).
Additionally, it is advisable to take inspiration from the Singaporean government, which has allocated a reserve fund of HKD 400 million to directly support the development of innovative technologies, especially cryptocurrency platforms.
· Providing Direct Support for the Development of Blockchain Technology in the Industry
To foster the growth of blockchain technology within various industries, a comprehensive support framework is essential. This framework should include the following initiatives:
- Specialized Funding: Allocate dedicated funds specifically for the development and deployment of blockchain technology. This funding should support initiatives related to smart contracts, digital asset trading, and cross-border payment solutions, which are crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and transparency in transactions.
- Funding for FinTech Startups: Increase financial backing for FinTech startups by offering low-interest loans or innovative grants. This support will assist these emerging companies in developing solutions such as digital payments, InsurTech, and RegTech, thereby contributing to the overall advancement of the financial technology ecosystem.
- Encouragement of Blockchain Applications: Actively promote and support the development of blockchain applications in areas such as corporate financing and asset management. By facilitating the integration of blockchain technology, businesses can improve their operational processes and increase trust among stakeholders.
- Funding for Cybersecurity R&D: Provide financial support for research and development initiatives focused on cybersecurity infrastructure related to digital finance. Emphasis should be placed on preventing cyberattacks and data breaches, ensuring that the adoption of blockchain technology does not compromise the security of financial transactions and sensitive data.
· Investing in Digital Currency Infrastructure:
- Amplifying Resources for e-HKD: Propel the financial backing for research initiatives and pilot projects centered around the “e-HKD” (the digital Hong Kong dollar). This strategic enhancement aims to catalyze the broader adoption of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC), ushering in a new era of digital finance that intertwines innovation with practical application.
- Synergy with Digital Renminbi: Foster a robust partnership in conducting cross-border payment trials alongside Mainland China's “Digital RMB.” This collaborative endeavor seeks to fortify the financial nexus with the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, paving the way for seamless transactions and an integrated economic landscape that transcends borders.
2. Supporting the Development of Digital Assets, Especially Virtual Assets
- Refining the Regulatory Landscape: Continuously enhance the regulatory framework governing virtual assets to cultivate market stability and security. In response to the shifting geopolitical and business climates, actively support or invest in local research and development of regulatory technology (RegTech). Allocate resources toward intelligent regulatory tools that empower financial regulators to adeptly navigate digital financial risks, thereby safeguarding the interests of consumers and investors alike.
- Bolstering Support for VASPs and VATPs: Amplify assistance for Virtual Asset Service Providers (VASPs) and Virtual Asset Trading Platforms (VATPs), focusing particularly on local legal and tax advisory services, along with tailored incentives to foster growth and compliance.
- Fostering Collaborative Synergies: Stimulate collaboration between financial institutions and tech innovators, paving the way for a seamless fusion of digital technology within traditional financial services, thus enhancing user experience and operational efficiency.
- Certification and Oversight of Virtual Asset Offerings: Advocate for the rigorous certification and regulation of virtual asset-related products, including cryptocurrency exchanges and virtual asset funds. Provide direct support to local regulatory authorities with resources—such as skilled personnel—to expedite and refine the review and licensing processes.
- Cultivating a Digital Finance Ecosystem: Enhance the visibility and appeal of the digital finance ecosystem by funding international FinTech summits, thereby drawing global digital finance companies and investors' attention to Hong Kong's burgeoning market.
- Establishment of a Digital Finance Demonstration Zone: Create a dedicated digital finance demonstration zone in Hong Kong, showcasing physical pilot operations for digital banks and virtual asset exchanges, thus serving as a beacon for innovation and experimentation in the realm of digital finance.
3. Expanding the Utilization of Digital Renminbi (e-RMB)
- Advancing Pilot Initiatives: Propel the initiation and practical application of the digital renminbi in Hong Kong, focusing on pivotal sectors such as financial securities, retail transactions, and cross-border payments. These pilot programs aim to showcase the versatility and efficiency of e-RMB in everyday financial interactions.
- Deepening Collaboration with Mainland China: Fortify partnerships with Mainland China to investigate the seamless integration of digital renminbi with Hong Kong's local payment frameworks. This collaborative effort seeks to enhance capital mobility throughout the Greater Bay Area, creating a more interconnected financial ecosystem.
- Fostering Regulatory Alignment: Advocate for synchronized efforts with Mainland authorities regarding digital financial regulation, data privacy, and technical standards. This coordination is essential for streamlining the integration of digital finance within the Greater Bay Area, ensuring a cohesive approach to digital currency implementation and governance.
4. Accelerating the Development of Digital Hong Kong Dollar (e-HKD)
Hong Kong should leverage its status as an international financial center to accelerate the development of e-HKD, establishing it as a model for global central bank digital currencies (CBDC) and further enhancing financial competitiveness. Ensuring its security, usability, and broad acceptance involves a multifaceted approach that includes technological innovation, policy support, and public participation. Specific measures are recommended as follows:
Technological Innovation
- Pilot Programs: Implement small-scale pilot programs to test the technical feasibility and application scenarios of e-HKD, including retail payments, cross-border payments, and financial transactions.
- Involvement of FinTech Firms: Engage FinTech companies to foster the development of innovative solutions.
- Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT): Introduce DLT and explore the use of blockchain technology to enhance transaction transparency, security, and efficiency. Test a multi-layer architecture where the central bank controls the core system while commercial banks or payment institutions operate the second layer network to ensure efficiency and scalability.
- Upgrade Digital Payment Infrastructure: Strengthen and upgrade digital payment infrastructure to support the high-frequency trading and low-latency requirements of e-HKD. Ensure seamless integration of e-HKD with existing payment systems (e.g., PayMe, Alipay, WeChat Pay, BOC Pay, and Faster Payment System).
- Enhance Cybersecurity: Invest resources in researching quantum-resistant encryption technologies to safeguard against future cyber threats. Establish comprehensive monitoring and emergency mechanisms to protect transaction data security and privacy.
Infrastructure Development
- Efficient Payment Ecosystem: Build an efficient payment ecosystem that includes developing payment terminals and applications supporting e-HKD, ensuring widespread adoption in retail payment scenarios, and advancing the digitization of cross-border payment and settlement systems to enhance Hong Kong's status as an international financial center.
- Cross-Border Applications: Promote cross-border applications by strengthening cooperation with Mainland China, piloting interoperability between e-HKD and the Digital Renminbi, and exploring cross-border payment collaborations with other countries' CBDCs to reduce currency exchange costs and time.
- Enhancing Financial Inclusion: Utilize e-HKD to lower the cost of electronic payments for merchants and individuals, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises and vulnerable groups. Provide user-friendly digital wallets to facilitate wider access to and use of e-HKD.
Policy Measures
- Clear Legal Framework: Develop a clear legal framework and regulatory system governing the use of e-HKD, covering anti-money laundering (AML), combating the financing of terrorism (CFT), and user privacy protection. Clarify the relationship between e-HKD and existing monetary policies to ensure no negative impact on financial stability.
- Alignment with International Standards: Align with international standards by referencing the development experiences of other CBDCs (e.g., China’s Digital Renminbi, European Central Bank’s Digital Euro). Participate in discussions and research on CBDCs led by international financial institutions (e.g., IMF, BIS) to ensure e-HKD meets global standards and can circulate as an international currency.
Public Participation
- Education and Outreach: Educate the public on the usage and advantages of e-HKD, such as transaction convenience, security, and privacy protection. Address public concerns regarding digital currencies, especially regarding personal privacy and financial stability.
- User Participation in Trials: Encourage user participation in pilot programs by offering economic incentives, such as cash rebates or discounts, to attract users to engage with e-HKD trials. Collect feedback from users to improve the experience.
- Transparent Communication Mechanism: Regularly update the public on the development progress of e-HKD to strengthen trust and support. Publicly disclose technical audits and pilot results to demonstrate the safety and reliability of e-HKD.
Timeline for Implementation
- Short-Term Goals (1-2 years): Complete technical testing and regulatory framework design.
- Medium-Term Goals (3-5 years): Achieve large-scale pilot applications.
- Long-Term Goals (5 years and beyond): Fully promote e-HKD to become a mainstream payment method.
To oversee the implementation process, it is recommended to establish a supervisory committee composed of government representatives, financial institutions, and experts responsible for monitoring the development progress and evaluating the effectiveness of e-HKD implementation. The expert group should comprise practitioners with hands-on experience rather than theoretical academics.
5. Attracting Global Digital Finance Enterprises and Talent
- Strategic Tax Incentives and Financial Support: Implement attractive tax incentives and financial subsidies designed to lure international digital finance firms to set up their headquarters or operational bases in Hong Kong. These incentives will serve as a catalyst for fostering a vibrant financial ecosystem.
- Streamlined Visa Processes: Enhance visa facilitation measures to draw elite technology and digital finance professionals from across the globe. By simplifying the immigration process, Hong Kong can effectively harness these talents to nurture and develop a robust pool of local expertise that meets international standards.
- Creation of Specialized Funds: Establish dedicated funds aimed at supporting the synergistic growth of local startups alongside foreign enterprises. This initiative will promote innovation within the financial technology sector, fostering a collaborative environment that drives cutting-edge advancements and enhances the overall digital finance landscape.
6. Promoting Green Digital Finance
- Incentivizing Financial Institutions: Inspire financial institutions to harness digital technologies for the creation and delivery of green finance solutions. For example:
- Innovative Green FinTech Solutions: Champion the development of environmentally friendly financial solutions powered by cutting-edge technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and big data. These innovations will enhance both the transparency and efficacy of green financial products, making them more appealing to investors.
- Creation of an Open Green Data Platform: Establish a comprehensive green data platform that prioritizes accessibility for local businesses, offering free access to vital information. This platform should consolidate environmental data, carbon emissions statistics, and corporate sustainability metrics, thereby facilitating informed decision-making.
- Facilitation of Blockchain Applications: Leverage blockchain technology to meticulously track the utilization of green assets, ensuring that allocated funds are directed toward projects adhering to stringent green standards. This transparency will significantly bolster investor confidence.
- Digital Evolution of Green Bonds and Financial Instruments: Promote the digital transformation of the green bond market and other sustainable financial assets to foster a landscape of sustainable finance. Digitizing green financial products is anticipated to yield substantial benefits, outweighing potential drawbacks. By employing blockchain platforms for green bond issuance, transaction costs can be reduced and efficiency enhanced. Furthermore, automating the certification process for green bonds through digital means will improve transparency and expedite issuance. A dedicated digital green bond platform will attract a broader spectrum of international investors to engage with Hong Kong's green finance market, thus channeling significant global capital into sustainable initiatives.
7. Strengthening Cybersecurity and Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
- Subsidizing Advanced Regulatory Solutions: While enforcing the adoption of compliant and secure regulatory tools, consider implementing subsidies or funding programs aimed specifically at financial institutions—particularly small and medium-sized enterprises—to facilitate their transition to cutting-edge regulatory technologies. This support will enable them to enhance compliance without incurring prohibitive costs.
- Cultivating Public-Private Partnerships: Encourage the formation of strategic alliances between public and private sectors to host regular summits and seminars centered on cybersecurity and regulatory technology. Such collaborations will not only attract funding and technological advancements to tech parks and high-tech development zones but will also provide local developers with opportunities to acquire expertise and knowledge from international sources.
- Promoting a Risk-Based Cybersecurity Framework: Advocate for financial institutions to implement a risk-based approach to cybersecurity, tailored to their specific capabilities and challenges. Provide assistance in crafting specialized cybersecurity strategies that address the distinct demands of the financial sector, encompassing areas such as risk assessment, vulnerability management, and incident response protocols.
- Government-Driven Cybersecurity Infrastructure Investment: The government should spearhead investments aimed at bolstering cybersecurity infrastructure within the digital finance realm, ensuring the integrity and security of digital transactions. Additionally, promoting the use of local cybersecurity tools and management solutions will foster a mutually beneficial profit-sharing ecosystem between public and private entities, reinforcing the overall resilience of the financial sector.
8. Education and Public Engagement
- Investing in Financial Literacy Resources: Dedicate increased resources to advance education in financial technology and digital finance. For instance, enhance outreach initiatives on platforms like “The Chin Family in the Investor and Financial Education Council’s,” aiming to deepen public comprehension and acceptance of digital payments, virtual assets, and cybersecurity measures. Moreover, motivate platforms and financial institutions to deliver relevant knowledge and training to the community, fostering a more informed citizenry.
- Collaborative Efforts with Academic Institutions: Forge partnerships with educational establishments to expand the curriculum around digital finance, thereby nurturing local talent in this burgeoning sector. Such collaboration will ensure that students are equipped with the necessary skills and knowledge to thrive in a rapidly evolving landscape.
- Engaging Industry Experts: Encourage local universities and colleges to invite seasoned industry professionals to share their insights through case studies and practical solutions. This engagement will enrich the academic experience for students and better prepare them for successful careers in the digital finance arena, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and real-world application.
Regarding to ESG
A Green Finance Revolution
In the bustling metropolis of Hong Kong, a mere 1% of electricity generation emanates from renewable sources. This startling statistic, sourced from the Hong Kong Energy Statistics Annual Report 2022, paints a picture of dependency on imported power—nuclear energy accounts for a substantial 28%, while the lion's share, 48%, thrives on natural gas. Meanwhile, across the globe, other financial hubs are outpacing Hong Kong in the renewable race. London's energy landscape is electrified with a 40% contribution from renewables, as highlighted in the UK Department of Energy 2023 Report. Across the Atlantic, New York strides forward with a commendable 20% as per the U.S. Energy Information Administration 2023 Report. Even Singapore, a city-state bathed in sunlight, is harnessing solar power to reach 4% of its energy production, according to the Energy Market Authority of Singapore 2023.
The message is clear: Hong Kong must sprint, not saunter, towards a greener future. The challenge? Achieving monumental advancements with prudent financial strategies. But fear not, for we have a blueprint, a roadmap, a vision. Specific yet strategic, our recommendations are poised to transform Hong Kong’s energy tapestry, weaving in threads of sustainability, innovation, and resilience. It's time to turn the tide, to light up the city with the power of the sun, the wind, and the waves. The journey begins now, for tomorrow's energy is in our hands today.
Strategic Recommendations for Advancing Hong Kong's Renewable Energy Landscape
1. Implement a Robust Long-term PPA Support Mechanism
To catalyze the growth of new energy projects, establishing long-term Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) is imperative. These agreements serve as a beacon of revenue stability, enticing private capital investment into the burgeoning field of renewable energy.
- Proposed Pricing Framework: Hong Kong should consider aligning its PPA pricing with international benchmarks, such as those in the UK and New York. A competitive rate of 1.2 HKD per kWh, translating to approximately 1,200 HKD per megawatt-hour, is recommended.
- Global Insights:
- The UK's 2023 Contracts for Difference (CfD) auction set an average PPA price for offshore wind at 500 HKD per megawatt-hour, approximately £50.
- In New York State, the offshore wind PPA price hovers around 650 HKD per megawatt-hour, roughly $83.
- Revenue Aspirations: Consider a 1 GW offshore wind project. Such an endeavor could yield an impressive 2.6 billion kWh annually, securing investors a stable revenue stream of 3.1 billion HKD. This initiative would significantly bolster Hong Kong's renewable energy quotient, steering the city towards a future where clean energy isn't merely an option but a standard.
2. Introduce Targeted Tax Incentives
To spur investment in Hong Kong's new energy sector, strategic tax incentives are essential. These measures should be tailored to enhance the financial appeal and viability of renewable energy projects.
- Profits Tax Exemption: Implement a 10-year profits tax exemption for projects focused on wind, photovoltaic, and energy storage systems. This initiative aims to amplify investment returns and attract more stakeholders to the renewable energy space.
- Streamlined Import Procedures: While Hong Kong already offers exemptions on most import duties, further simplification of import procedures is crucial. By reducing logistics time and associated costs, the importation of new energy equipment can be expedited, facilitating quicker project deployments.
- Global Comparisons:
- In Singapore, corporate income tax exemptions range from 5 to 15 years, as highlighted by the Energy Market Authority of Singapore 2023.
- Vietnam offers a 13-year tax rate reduction specifically for new energy projects, according to the PwC Vietnam Tax Handbook 2024.
These incentives not only align Hong Kong with international best practices but also position it as a competitive player in the global renewable energy arena.
3. Incentives for Land and Offshore Area Usage
To facilitate the growth of offshore wind and photovoltaic power projects, providing advantageous land and sea area usage rights is crucial. This approach would enable the development of substantial renewable energy infrastructure in strategic locations.
- Proposed Locations and Capacities:
- Southeastern Waters of Hong Kong: Ideal for establishing a 1,000 MW offshore wind farm, this area has the potential to generate approximately 2.6 billion kWh annually.
- Dapeng Bay: This location can support a 500 MW wind farm, contributing significantly to the region's renewable energy output.
- Southern Waters of Lamma Island: With the capacity for a 300 MW wind farm, this area offers further opportunities for renewable energy expansion.
- Global Benchmark:
- In the Netherlands, the government provides free usage rights for offshore wind farms in the North Sea, according to the Netherlands Renewable Energy Association 2023.
By offering these incentives, Hong Kong can attract significant investments and expertise, aligning its renewable energy strategies with successful international models. This initiative would not only enhance energy security but also cement Hong Kong's status as a leader in sustainable development.
4. Support for Shared Cable Construction Costs
Offshore wind projects necessitate the installation of submarine cables to integrate with the grid, which represents a significant portion of the total investment—approximately 15% to 20%.
- Recommendation: To reduce the financial barrier for investors, the government could subsidize 30% to 50% of the cable construction costs. This support would effectively lower the initial investment threshold, making these projects more financially feasible.
- Global Insight:
- European North Sea wind farms have demonstrated that governmental funding for grid infrastructure can significantly boost private investment, as noted in the International Energy Agency 2023 Report.
By adopting this approach, Hong Kong can stimulate private sector involvement in offshore wind projects, fostering innovation and accelerating the transition to renewable energy. This collaborative model would enhance the city's energy infrastructure while promoting sustainable economic growth.
5. Expand Green Bonds and Bank Loans
To further propel the growth of renewable energy projects in Hong Kong, an expansion of the Hong Kong Green Bond Program, along with the introduction of dedicated low-interest green loans, is recommended.
- Funding Objectives: These financial instruments should be directed towards the development of wind power, photovoltaic power generation, and energy storage infrastructure. By doing so, they will provide the necessary capital to drive innovation and expand the city's clean energy capabilities.
- Global Benchmarks:
- In 2023, Singapore issued green bonds amounting to USD 3.5 billion, as reported by the Government of Singapore.
- The European Investment Bank consistently provides around EUR 5 billion annually in green loans to support infrastructure development, according to their 2023 Report.
By following these international examples, Hong Kong can significantly enhance its renewable energy financing mechanisms. This strategic expansion will not only attract more investors but also ensure that Hong Kong remains at the forefront of sustainable finance and development.
6. Establish a Green Infrastructure Fund
The creation of a Green Infrastructure Fund is essential for supporting local renewable energy projects and attracting international investment into Hong Kong's new energy sector.
- Background and Necessity:
- Currently, Hong Kong lacks a cohesive green infrastructure funding platform, which restricts the financial integration and scalability of new energy initiatives.
- By establishing a Green Infrastructure Fund, Hong Kong can alleviate early-stage funding pressures and draw in substantial private capital, thereby enhancing project viability and sustainability.
- Successful Global Models:
- UK Green Investment Bank (GIB): With an initial funding pool of £3 billion (approximately HKD 30 billion), the GIB successfully attracted private capital amounting to three times its initial investment, illustrating the power of leveraging public funds to catalyze private sector participation.
- Singapore Green Infrastructure Fund: With an initial scale of USD 2 billion (approximately HKD 15.6 billion), this fund is dedicated to advancing solar and energy storage projects across the Asia-Pacific region, showcasing a focused approach to regional clean energy advancement.
By adopting a similar strategy, Hong Kong can create a robust financial ecosystem that not only supports local renewable projects but also positions the city as a key player in the global green finance landscape. This fund would act as a magnet for international investors, fostering innovation and sustainable development within the region.
7. Establish a Dedicated Department and Set KPIs
Creating a specialized department focused on new energy development is crucial for coordinating efforts and achieving strategic energy goals in Hong Kong.
- Objectives:
- Renewable Energy Target: Aim to increase the proportion of renewable energy in Hong Kong to 15% by 2035.
- Offshore Wind Capacity: Develop and achieve an installed capacity of 3 GW in offshore wind power by the same year.
- International Benchmark:
- The UK's National Infrastructure Commission (NIC) serves as a model, with its annual energy progress reports that drive policy implementation and accountability.
By establishing this dedicated department, Hong Kong can ensure focused oversight and efficient management of renewable energy projects. Setting clear Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) will guide progress, facilitate transparency, and ensure that the city meets its ambitious energy targets. This strategic move will align Hong Kong with global best practices in energy governance and policy execution.
8. Simplify Project Approval Process
To enhance the efficiency of new energy project deployments in Hong Kong, it is crucial to streamline the approval process, reducing the timeline from the current 36-48 months to 12-18 months. This can be achieved by adopting best practices from Mainland China, which are known for their efficiency in project approvals.
Policy Benefits:
1. Support for Achieving the 15% New Energy Target:
- By expediting the approval process, offshore wind, photovoltaic, and energy storage projects can collectively contribute an additional 2 GW of renewable energy capacity annually. This acceleration will play a significant role in reducing carbon emissions and reaching Hong Kong's renewable energy goals.
2. Promotion of Green Finance:
- Establishing a Green Infrastructure Fund and expanding the green bond program can attract substantial international capital to Hong Kong.
- By fostering collaboration with global institutions such as the Asian Development Bank and the European Investment Bank, Hong Kong can position itself as a leading green finance hub within the Asia-Pacific region.
3. No Increased Fiscal Pressure:
- The strategy recommends leveraging market mechanisms, with the government providing essential policy support and initial funding. This approach encourages the involvement of private capital, thereby reducing the fiscal burden on public finances.
By simplifying the project approval process and implementing these strategic benefits, Hong Kong can accelerate its transition to a more sustainable energy future, all while maintaining fiscal responsibility and enhancing its status as a green finance leader.
Sum Up
The advancement of new energy technologies stands as a pivotal cornerstone for Hong Kong's ambitious energy transformation. This shift is not merely a regulatory formality; it is a strategic maneuver that can significantly bolster the region's standing in the realm of green finance. Imagine the potential unleashed by the establishment of a robust green infrastructure fund! Coupled with enhanced policy support mechanisms and a simplification of approval processes, these initiatives could dramatically elevate the share of renewable energy sources in Hong Kong's energy mix.
As the city positions itself as a beacon of international green finance, the implications are profound. The journey towards long-term sustainable development is fraught with challenges, yet the rewards—both environmental and economic—are undeniably compelling. In this dynamic landscape, innovation and adaptability will be crucial, paving the way for a greener, more resilient future.
Conclusion:
As Hong Kong charts its fiscal path for the 2025-26 period, the city stands at a crossroads that requires strategic foresight and decisive action. The examination of its fiscal policies reveals underlying vulnerabilities tied to a narrow revenue base and persistent structural deficits. Addressing these challenges necessitates a multifaceted approach, focusing on diversifying revenue sources and implementing sustainable fiscal policies. The government must prioritize long-term planning and innovative financial strategies to stabilize and strengthen Hong Kong's economic foundation.
By expanding the tax base and refining expenditure management, Hong Kong can mitigate the risks associated with its current fiscal structure. Moreover, embracing transparency and responsible fiscal governance will be crucial in maintaining the city's esteemed status as a global financial hub while safeguarding the welfare of its citizens. As the government prepares to unveil the new budget, it is essential to incorporate insights from diverse stakeholders, fostering a collaborative effort to drive economic development and implement practical, future-oriented solutions. In doing so, Hong Kong can secure a resilient economic future, poised to thrive amidst global uncertainties.
If you have any inquiries regarding this letter, please feel free to contact me or Mr. LIU Tsan Pui Martin, the Director of the Industrial Relations Department.
Your Sincerely,
Mofiz Chan
Chairman
Hong Kong Securities and Futures Professionals Association
Latest Advocacy Papers
Opinion letter of 2026-27 Budget
2026-01-19


